Digital to Analog Signal Conversion Explained
Digital to analog signal conversion involves the process of changing or modifying one of the characteristics of an analog signal in accordance to the information in the digital data.
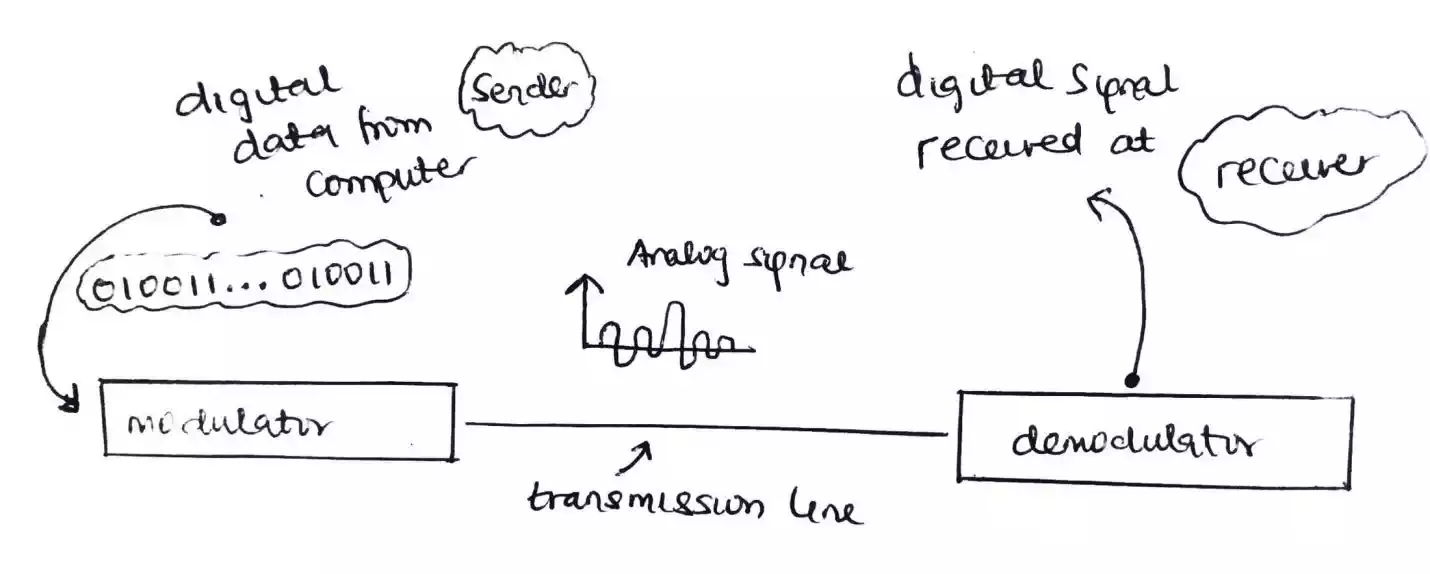
But before discussing on what the techniques used for converting a digital signal to analog signal lets first discuss on what digital and analog signals are.
Digital signalsare signals that carries information (data) in form of sequence of pulses with discrete value. Thus it occurs at discrete time. While
Analog signals are signals that carries information (data) which is continuous and have value at any instant of time.
Techniques for digital to analog conversion of signals
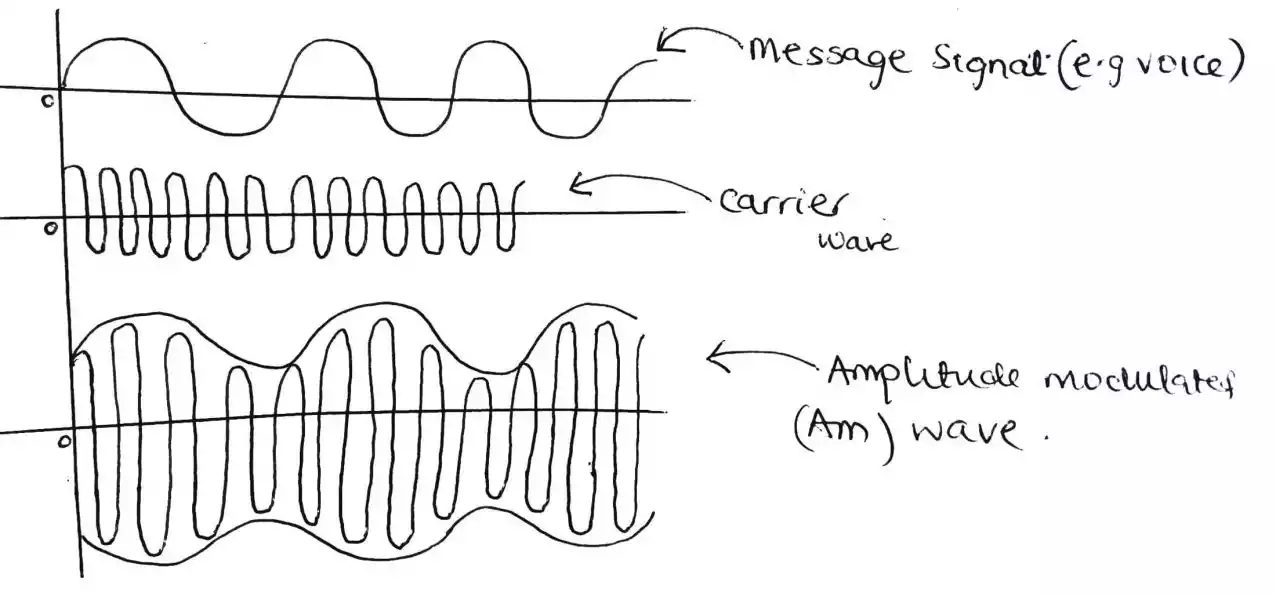
In a digital to analog conversion a carrier wave (sine wave) is modulated or modified based on the data of the digital signal.
As we all know that a sine wave is defined by amplitude, frequency and phase, this yield the following types of digital to analog conversion techniques.
- Amplitude shift keying (ASK)
- Frequency shift keying (FSK)
- Phase shift keying (PSK)
- Quadrature amplitude shift keying (QAM)
Note if you are familiar with modulation, shift keying is same but used in the digital world as oppose to modulation used in the analog world.
amplitude shift keying (ASK)
In amplitude shift keying, the amplitude of the carrier waves or signal is varied based on the digital signal while other parameters (frequency and phase) are kept constant.
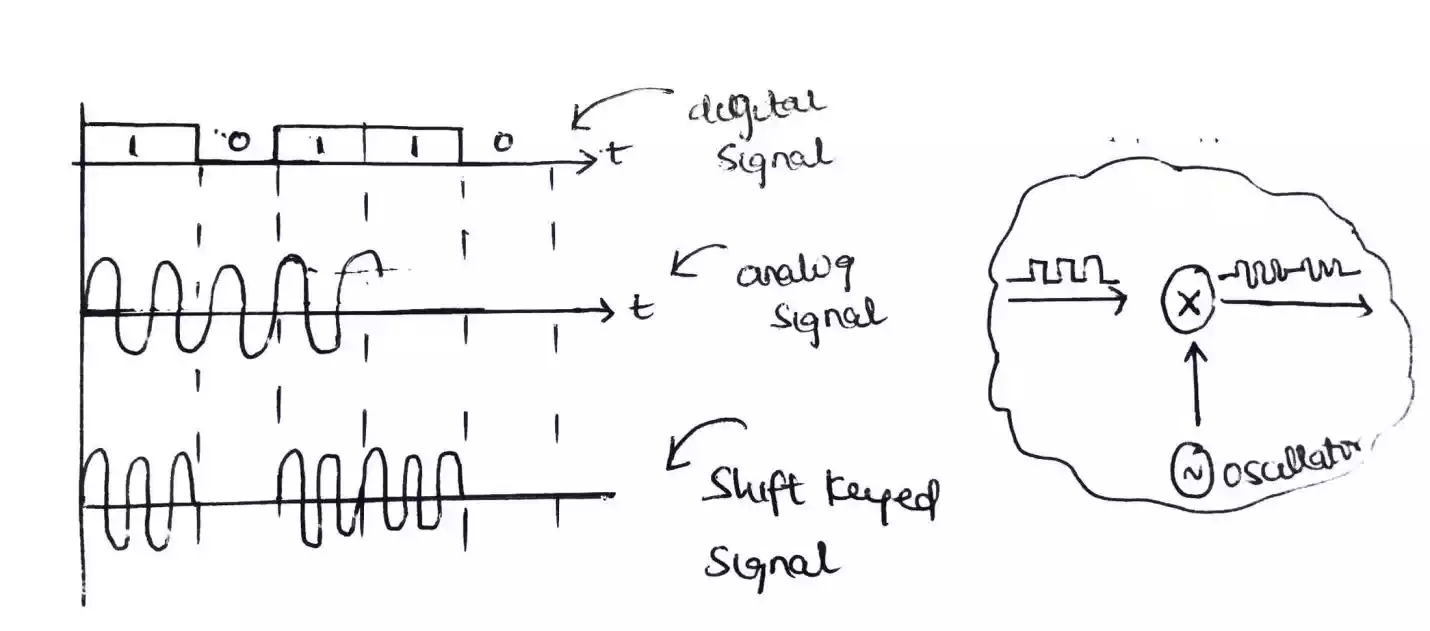
Advantages of amplitude shift keying (ASK)
As only one carrier wave is used,
The design is simple and inexpensive
The bandwidth is lesser compare to FSK which uses two carrier wave.
Disadvantage(s) of amplitude shift keying (ASK)
- It is more susceptible to noise as noise which is an interference has a low frequency and also affect amplitudes hence it will be difficult to differentiate between the real information and the noise.
frequency shift keying (FSK)
In frequency shift keying, the frequency of the carrier waves or signal is varied based on the digital signal while other parameters (amplitude and phase) are kept constant.
As oppose to ASK where a single carrier wave is modulated or shift keyed, two carrier waves with different frequencies are used. Where one is denoted as f1 which is of a high frequency that the second carrier denoted as f2. F1 is used when there is a one in the digital signal due to its high frequency while F2 is used for a 0 or low in the digital signal as f2 is a low frequency carrier.
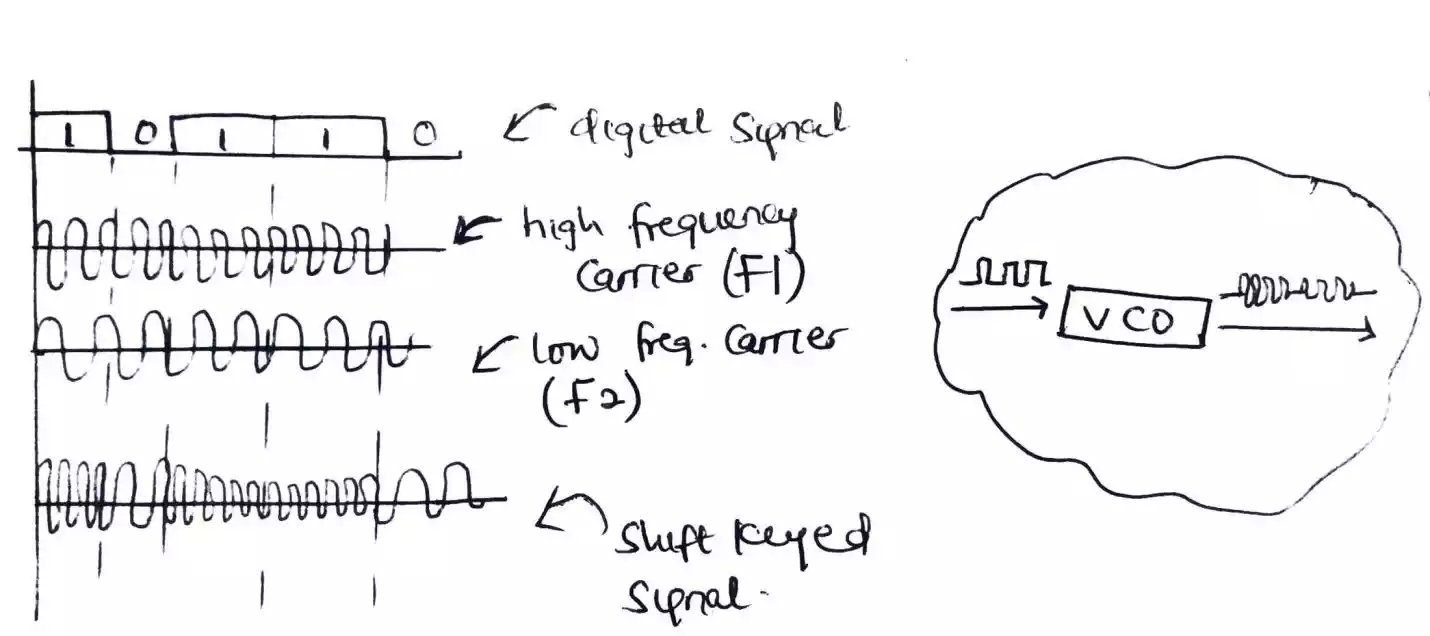
The device used to sense if there is low or high in the digital signal and send the corresponding carrier is a voltage controlled oscillator (VCO).
Advantages of frequency shift keying (FSK)
It is less susceptible to noise as noise occurs on the amplitude but the information in FSK is on the frequency.
There is the presence of high signal to noise ratio (SNR)
Disadvantage(s) of frequency shift keying (FSK)
- Due to two frequencies (carrier waves) used there is larger bandwidth consumption than ASK.
phase shift keying (PSK)
In phase shift keying, the phase of the carrier waves or signal is varied based on the digital signal while other parameters (frequency and amplitude) are kept constant.
Just as two frequencies are used in FSK, two phases are use in PSK one is starting at 0⁰ if there is a one or high in the data signal (i.e. 1 bit) and 180⁰ if there is a zero or low (i.e. 0 bit) in the data signal.
Also, the digital signal used is a polar NRZ signal meaning instead of having it values on one side of the time axis as in ASK and FSK, it has its value lying on both the up and down side of the time axis as shown.
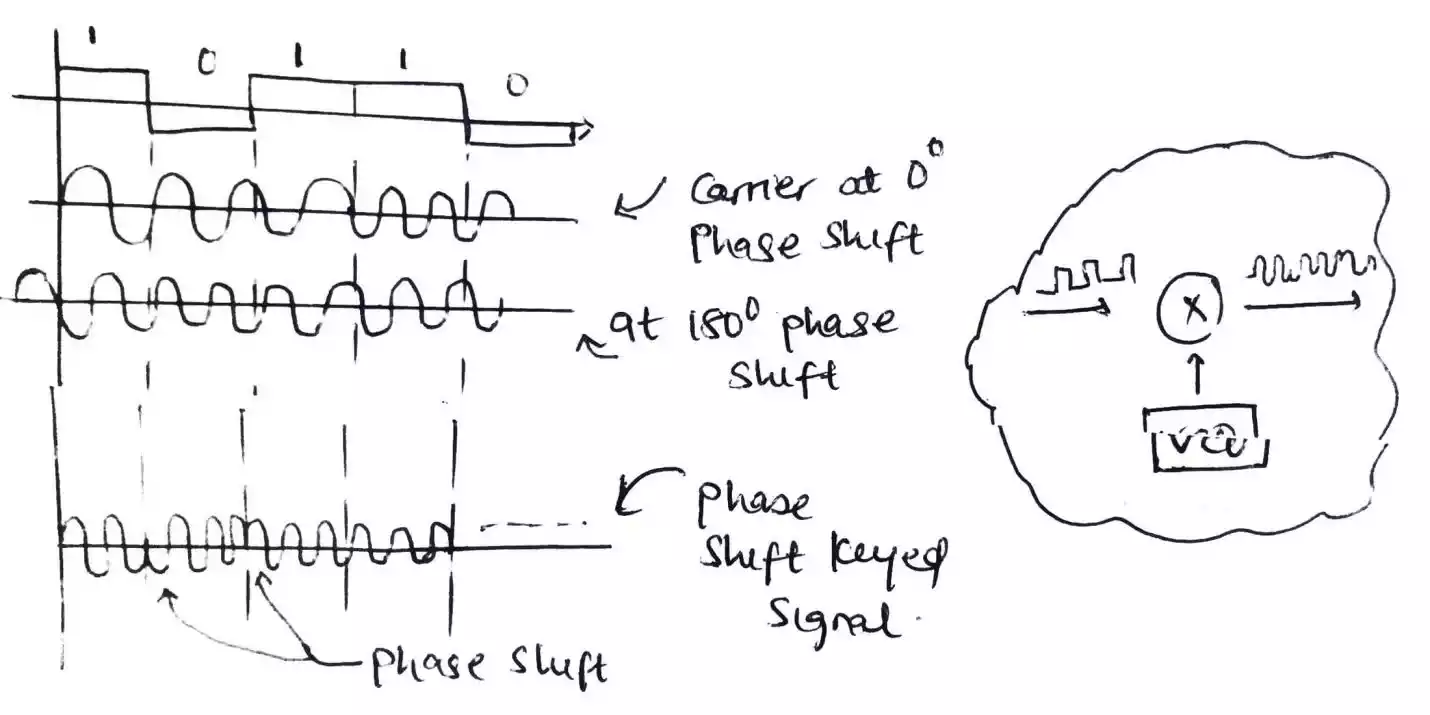
Same as in PSK, the device used to sense if there is low or high in the digital signal and send the corresponding carrier with different phase angle is a voltage controlled oscillator (VCO).
Advantage(s) of frequency shift keying (PSK)
- It is quite better than ASK and FSK due to its high efficiency.
Disadvantage(s) of frequency shift keying (PSK)
- The efficiency of its bandwidth is low.
quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM)
A quadrature amplitude modulation or shift keying, involves the combination of both ASK and PSK.
Advantage(s) of quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM)
- As it entails that QAM consist of ASK and PSK, it has the same advantages as ASK and PSK.
Disadvantage(s) of quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM)
- It can be said to be complex and expensive due to the combination of ASK and PSK.
Some asked questions
How are digital signals converted to analog?
A digital signal can be converted to an analog signal by modifying or shift keying one of the parameter of the carrier wave.
Why do we need to convert digital data to analog?
Digital signals need to be converted to analog because most modern technologies or devices understand digital data or signal but as the signals needs to be transmitted or radiated into space by an antenna, it needs to be converted to analog as free space understands analog data’s or signals.
Recommended for more exlanation:
📖 Data Communications
and Networking by Behrouz A. Forouzan