What Are the Advantages of Digital Modulation Over Analog Modulation?
Modulation is the process of modifying a carrier wave to encode information for transmission. The carrier wave is a high-frequency signal that is used to carry the information signal from the transmitter to the receiver.
Without modulation, the information, or message signal would not be able to travel over long distances, as the message signal is often a low frequency signal.
What Is an Analog Modulation?
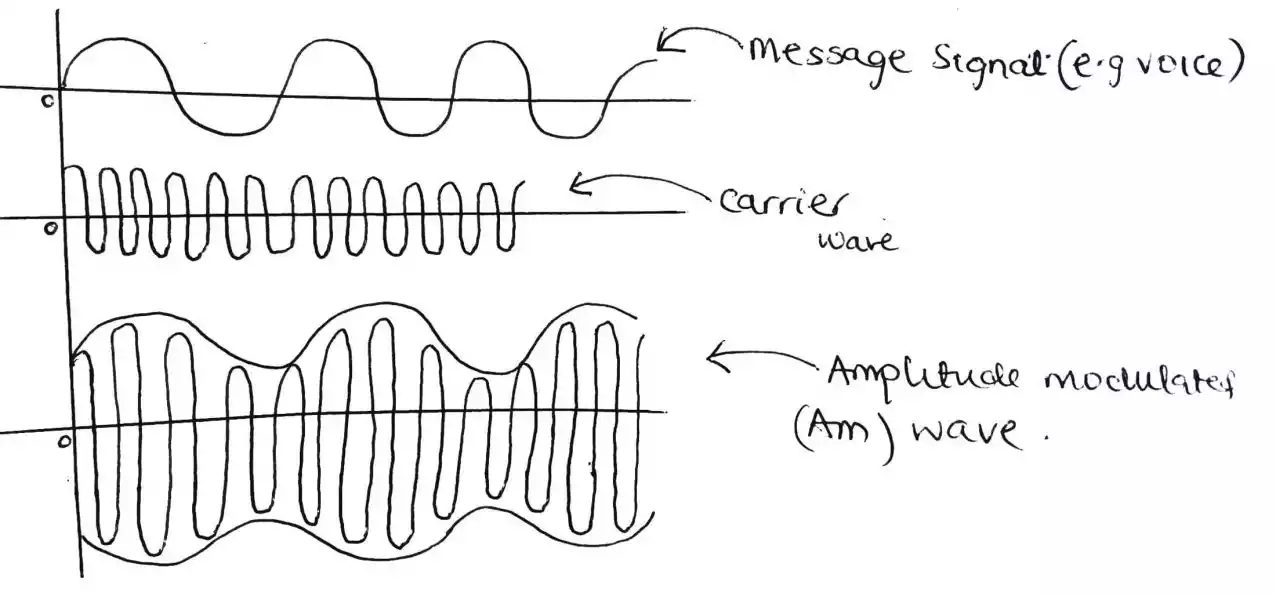
Analog modulation involves varying the amplitude, frequency, or phase of the carrier wave to encode the information signal. Examples of analog modulation techniques include amplitude modulation (AM), frequency modulation (FM), and phase modulation (PM).
These techniques are typically used to transmit analog signals, such as voice or music.
What Is a Digital Modulation?
Digital modulation involves encoding the information signal into a series of digital bits (0’s and 1’s), which are then transmitted by varying the amplitude, frequency, or phase of the carrier wave.
Examples of digital modulation techniques include pulse amplitude modulation (PAM), phase shift keying (PSK), and quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM). These techniques are typically used to transmit digital signals, such as data or digital voice.
Read on: What Is Modulation In Communication? Why Do We Modulate And The Types of Modulation Techniques?
What Are the Advantages of Digital Modulation Over Analog Modulation?
Digital modulation has several advantages over analog modulation, and the advantages are explained below:
- Better noise immunity – Digital modulation techniques, such as pulse amplitude modulation (PAM), phase shift keying (PSK), and quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM), can be designed to include error-correction codes that allow the receiver to detect and correct errors introduced by noise during transmission.
These error-correction codes enable digital signals to be transmitted with higher reliability and lower error rates than analog signals.
On the other hand, analog signals are more susceptible to noise and interference, and error-correction techniques are less effective. - More efficient use of bandwidth – Digital modulation techniques enable the transmission of information using less bandwidth than analog modulation techniques. This is because digital signals can be compressed and encoded in a more efficient manner.
For example, digital audio signals can be compressed using techniques such as MP3, which reduces the amount of data required to represent the audio signal without significantly affecting the perceived quality.
Analog signals, on the other hand, require a higher bandwidth to transmit the same amount of information, which can lead to more congested communication channels. - Improved security – Digital signals can be encrypted, making them more secure than analog signals.
Encryption involves the use of algorithms that scramble the digital signal in a way that can only be decoded by a receiver that has the correct key.
This makes it more difficult for unauthorized users to intercept and decode the signal. In contrast, analog signals can be intercepted and decoded more easily using devices such as radio scanners. - Flexibility – Digital modulation techniques enable the transmission of a wide range of data types, including voice, video, and data. This is because digital signals can be represented as binary numbers, which can be easily processed by digital systems such as computers and networks.
Analog modulation techniques, on the other hand, are limited to the transmission of audio and video signals. - Ease of integration – Digital signals can be easily integrated with other digital systems, such as computers and networks, making them more compatible with modern communication technologies.
This enables the integration of communication systems with other digital systems, such as the internet, allowing for the seamless transfer of information between different systems.
In general, digital modulation has several advantages over analog modulation, including better noise immunity, more efficient use of bandwidth, improved security, flexibility, and ease of integration with other digital systems.
As a result, digital modulation is becoming increasingly popular in modern communication systems. However, analog modulation is still used in certain applications, such as broadcasting and voice communication.