What Is Horn Antenna? Its uses, Types, Design parameters and Applications.
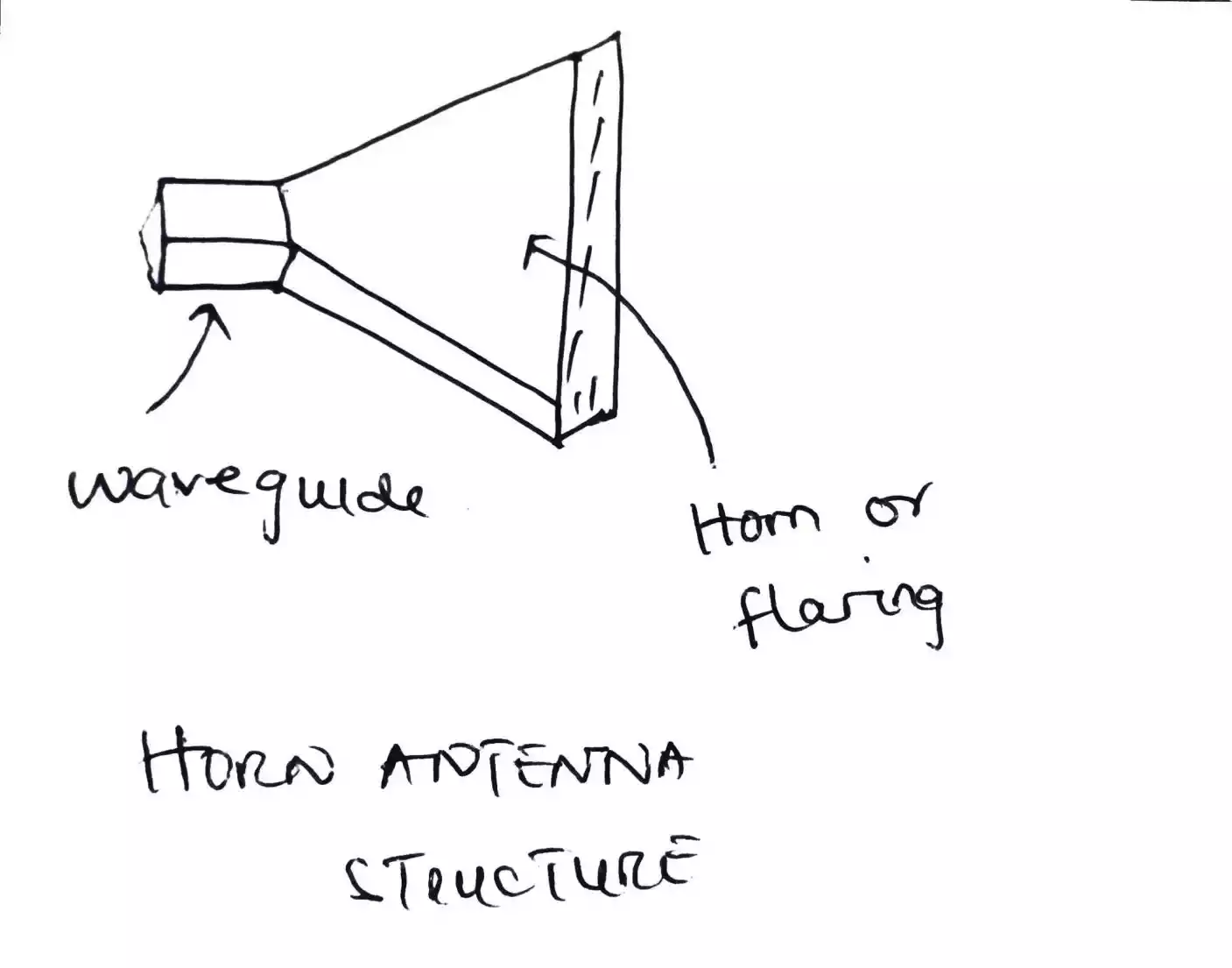
Horn antenna is an antenna which is constructed by flaring (or opening) of a waveguide (a metallic material) in order to direct electromagnetic waves in one direction.
What is a horn antenna used for?
It is a directional antenna which is used to increase directivity It helps in improving impedance matching because the waveguide mostly has impedance of about 50Ω while the impedance of the free space is 377Ω. In order to match out the impedance so as to reduce power loss, a flaring is used to kind of concentrate the electromagnetic waves. It is used for long distance communication due to its directivity
Structure of horn antenna
Analysis and design parameter of horn antenna
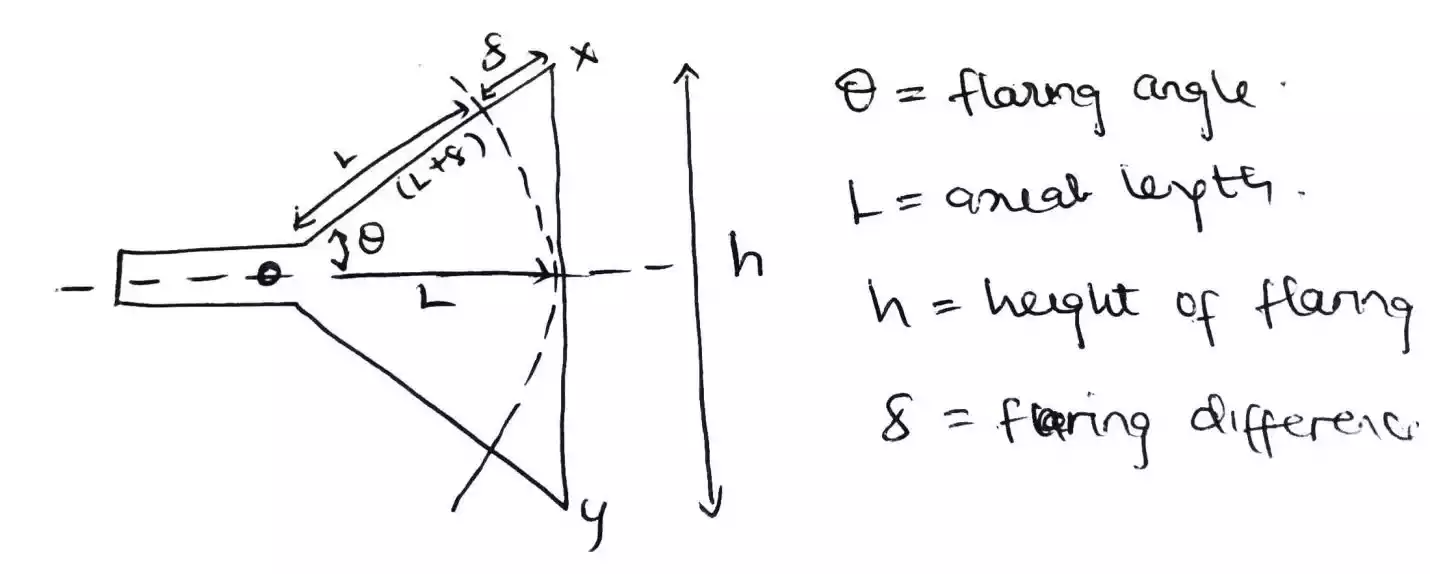
The figure above shows a cross section diagram of horn antenna along the E-plane which can be used to analyze its parameters such as the flaring angle theta, the axial length L, the height of flaring or aperture H.
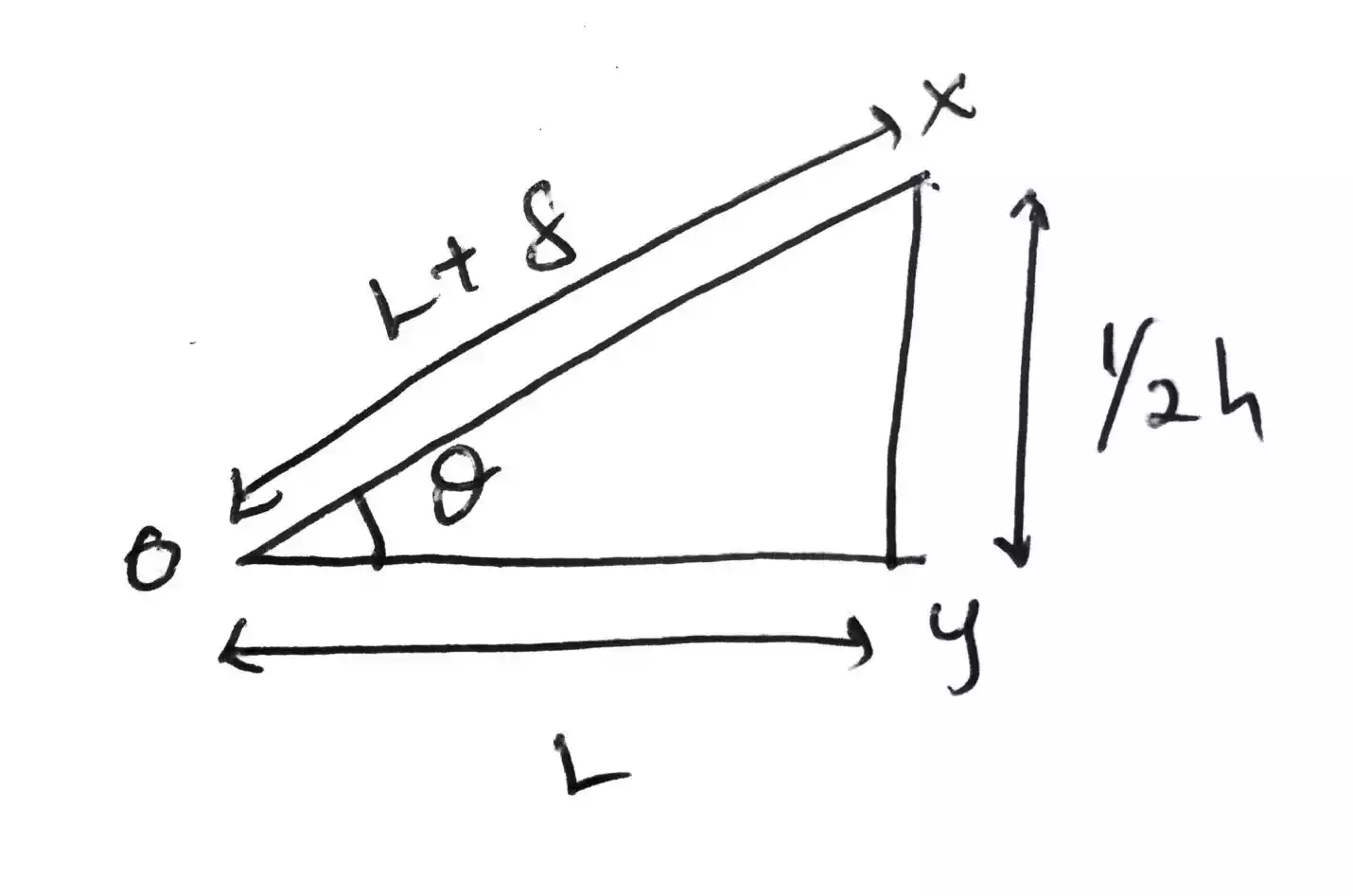
To find the axial length, we use Pythagoras theorem on the triangle ∠XOY
(L + δ)2 = L2 + (1/2h)2 L2 + 2Lδ +δ2 = L2 + (1/2h)2 ; expanding the bracket As δ is very small compared to L, we neglect δ2 as it will be even smaller L2 + 2Lδ = L2 + (1/2h)2 L2 - L2+ 2Lδ = + (1/2h)2 2Lδ = h2/4 L = h/8 δ
To find the flare angle, we can use either tanθ or cosθ depending on the known variable
Tanθ = opp/adj = (1/2h)/L = h/2L or Cosθ = adj/hyp = L/(L + δ) Hence θ has it expression in terms of L and δ if cosine of the angle is used or in terms of h and L if tangent of the angle is used.
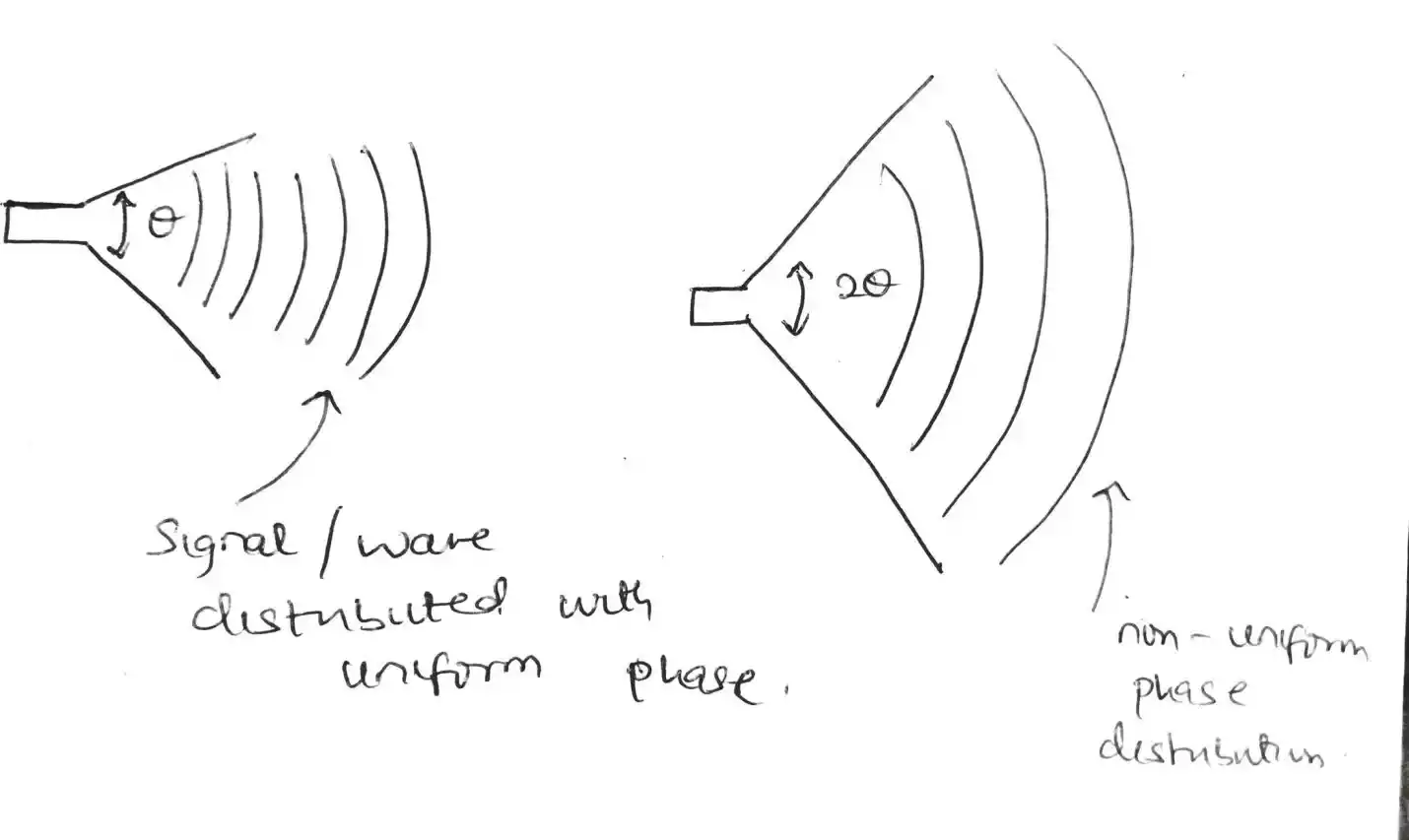
If the flare angle is small, there is uniform phase distribution as the beamwidth is small which also result in increase directivity.
Directivity ∝ 1/beamwidth or Directivity ∝ 1/aperture area
If the flare angle is doubled, the directivity is reduced due to high beamwidth which then result in non-uniform phase distribution.
Design of horn antenna
-
HPBW E – plane = 56°λ/A
where, A is area of aperture ( h x w(width) ) HPBW is Half Power BeamWidth and -
FNBW is First Null BeamWidth
-
HPBW H – plane = 67°λ/A
-
FNBW E – plane = 115°λ/A
-
FNBW H – plane = 115°λ/A
Directivity D, = 7.5A/ λ2
Gain, G = (4πA/ λ2) x η where η is characteristic impedance
Types of horn antenna
It be categorized as
- Sectoral horn antenna
- Pyramidal horn antenna
- Conical horn antenna and Bi-conical horn antenna
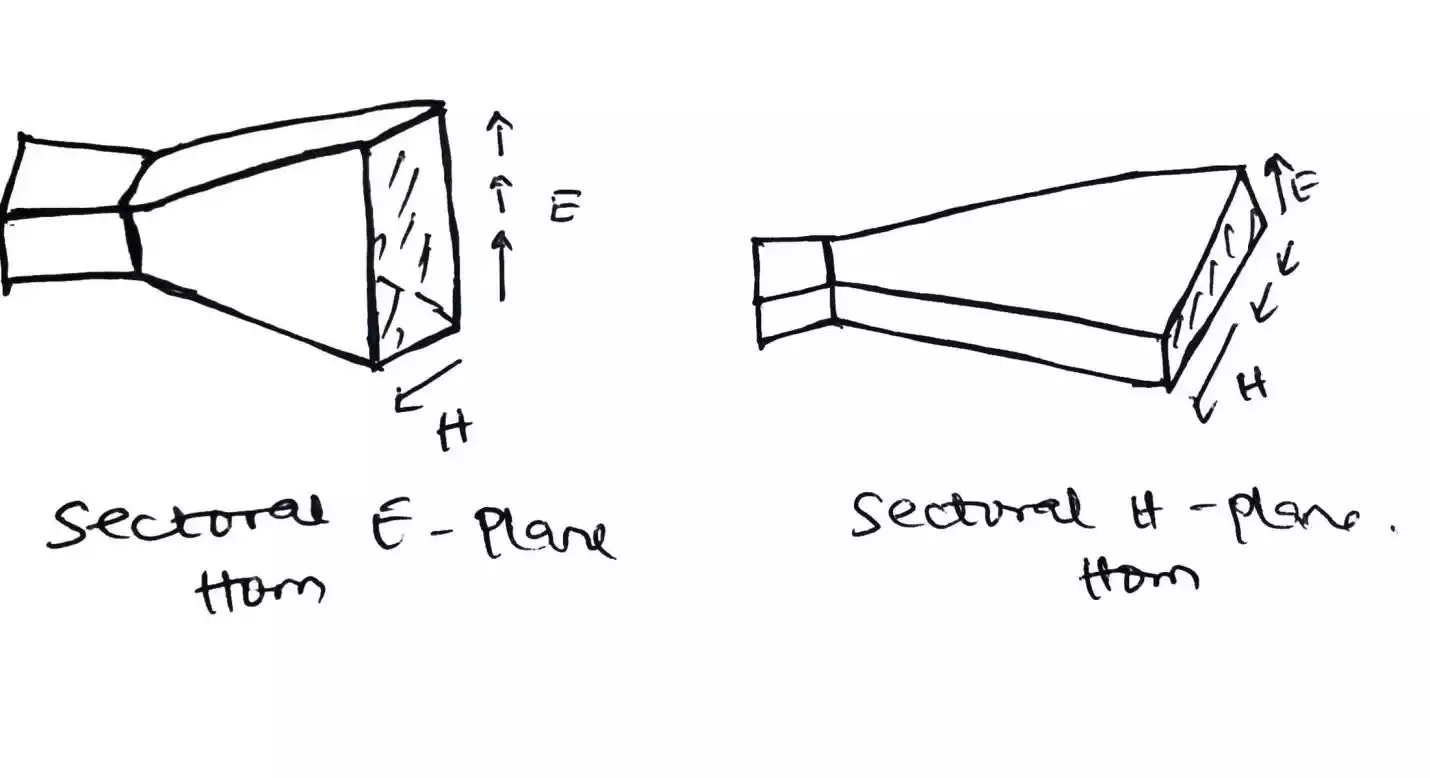
Sectoral horn antenna
This type of antenna has its flaring in one direction. It is of two types
a) sectoral E-plane horn antenna
b) sectoral H-plane horn antenna
Sectoral E-plane horn antenna
It has it flaring in the E (Electric field) direction i.e. the flaring is parallel to the E -plane.
Sectoral H-plane horn antenna
It has it flaring in the H (Magnetic field) direction i.e. the flaring is parallel to the H -plane.
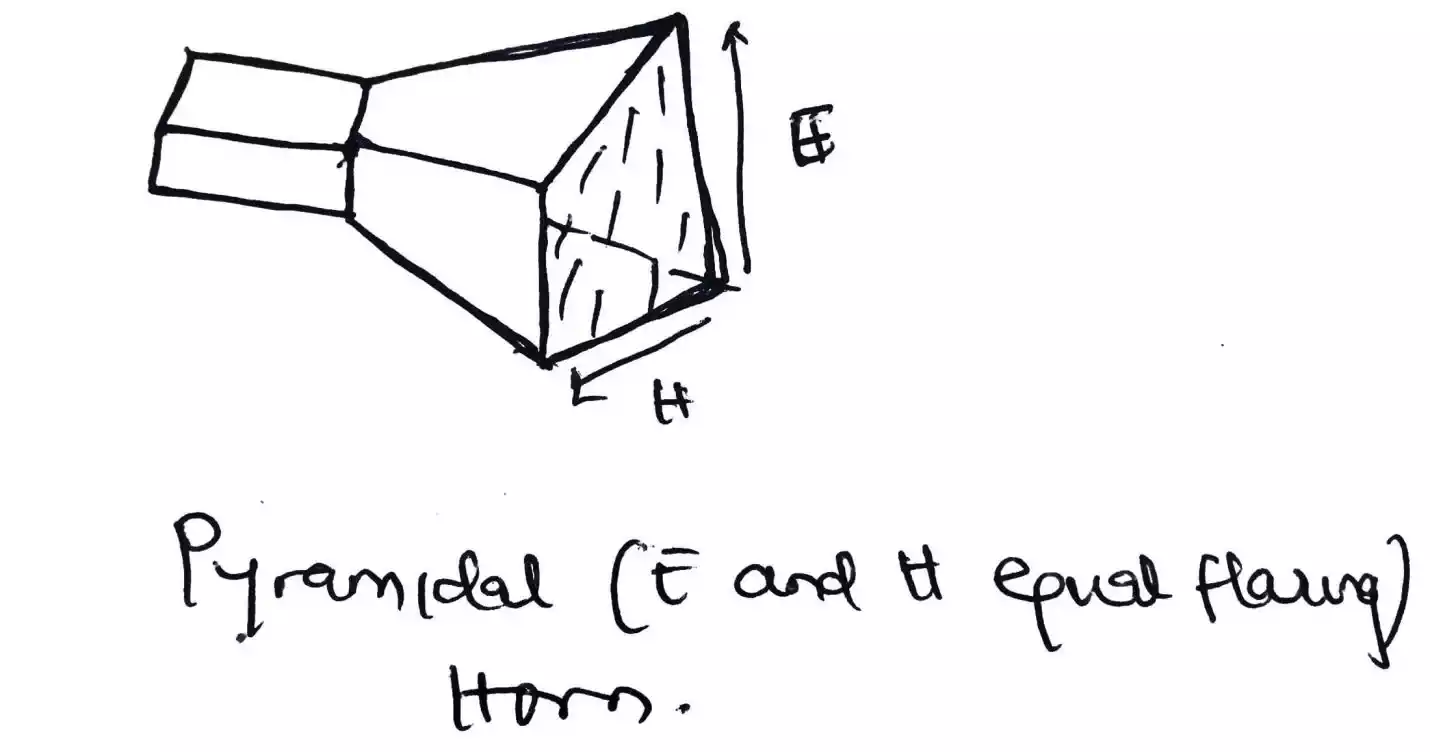
Pyramidal horn antenna
It has the flaring in both directions (i.e. both in the E-plane and H-plane direction)
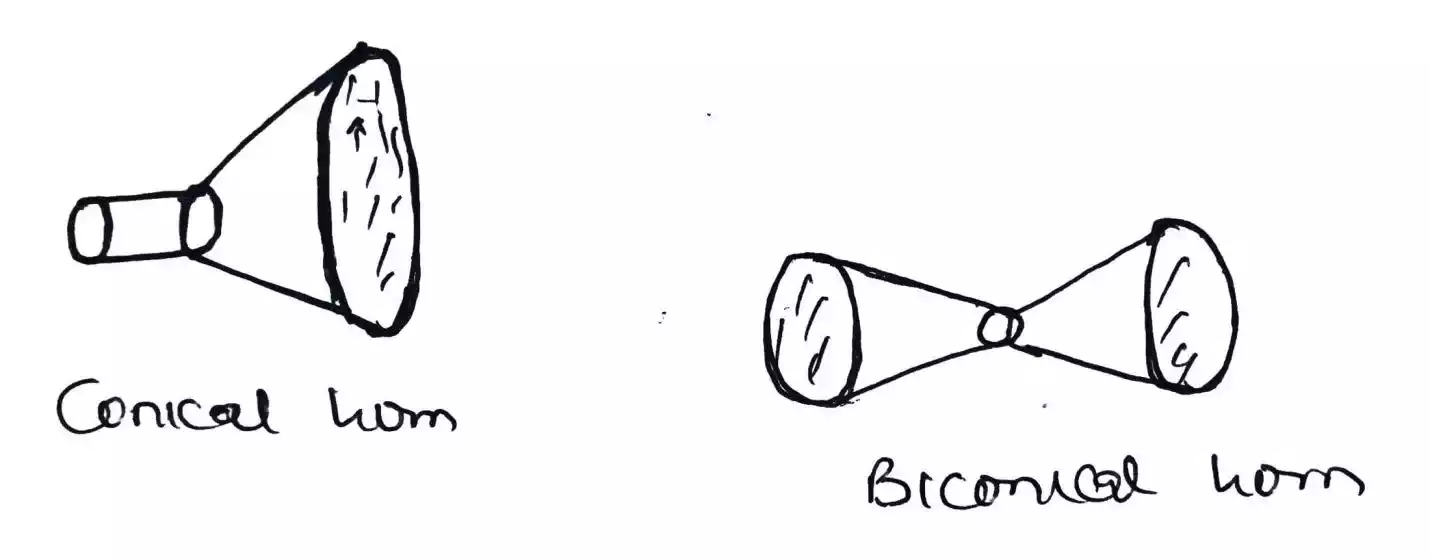
Conical horn antenna
It has cone like shape as its flaring and the waveguide is in a cylinder shape.
Bi-conical antenna
It consists of two conical antennas merged together.
Applications of horn antenna
In addition to the uses of horn antenna discussed above, here are some of its other applications
- It is used for microwave application
- It is used in satellite communication
- It is used as the active element (feed horn) in a dish antenna to receive the reflected wave.
- Horn antenna works in the Ultra High Frequency (UHF) 300Mhz and Super High Frequency (SHF) 30Ghz range.
- It is used for short range RADAR