Difference Between Linear and Nonlinear Devices
In electronics, a linear device is one that produces an output signal that is directly proportional to the input signal, whereas a nonlinear device is one that does not exhibit a direct proportionality between the input and output signals.
What Is a Linear Device?
A linear device is one that produces an output signal that is directly proportional to the input signal. This means that if the input signal is doubled, the output signal will also be doubled.
In another example, if you apply an input voltage of 5 volts to a linear amplifier, the output voltage will be proportional to the input voltage, such as 10 volts, assuming the amplification factor is 2.
In other words, the device responds to changes in the input signal linearly.
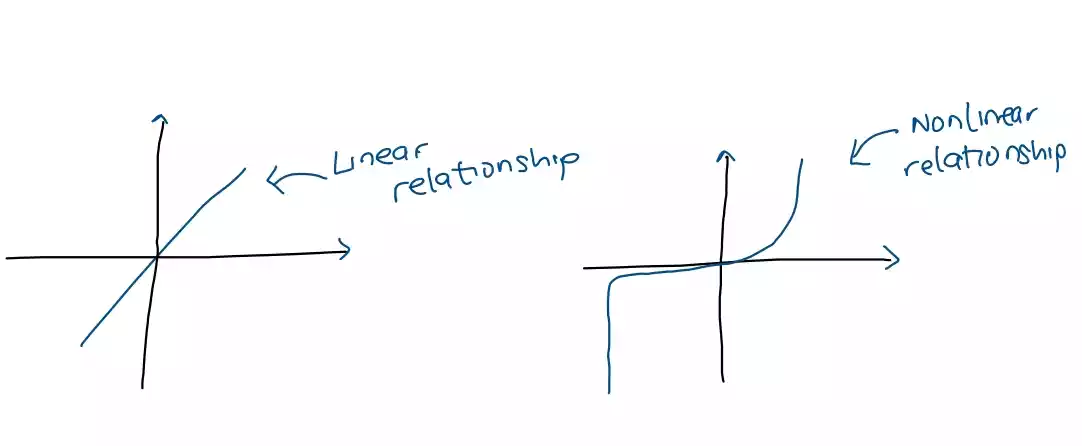
Linear devices exhibit a linear relationship between the input and output signals, which can be expressed as a straight line when plotted on a graph.
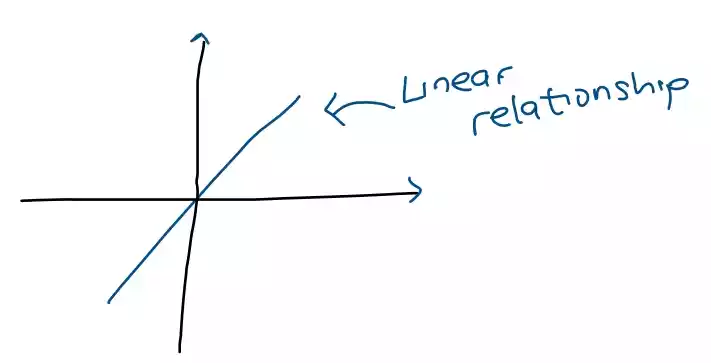
Examples of linear devices include resistors, capacitors, and inductors, as well as linear amplifiers and filters. These devices exhibit linear relationships between the voltage or current applied to them and the resulting voltage or current that they produce.
Linear devices are commonly used in signal processing applications where a close reproduction of the input signal is required.
What Is a Nonlinear Device?
A nonlinear device is one that does not exhibit a direct proportionality between the input and output signals. This means that the output signal may exhibit more complex behavior, such as generating harmonics, creating distortion, or even exhibiting chaotic behavior.
Nonlinear devices do not exhibit a linear relationship between the input and output signals, and the resulting plot of their input-output characteristics may be curved or non-monotonic.
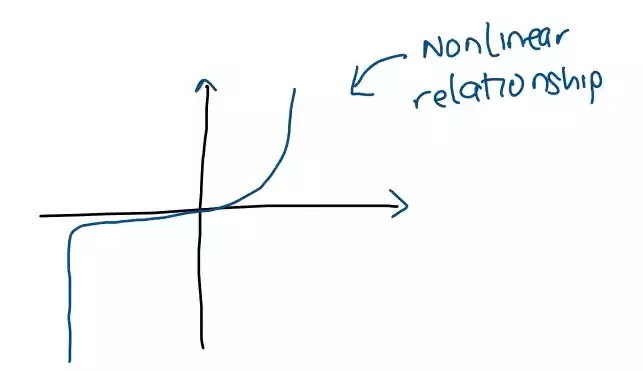
Examples of nonlinear devices include diodes, transistors, operational amplifiers and nonlinear amplifiers and filters, as well as devices that exhibit chaotic behavior, such as the Lorenz system.
These devices exhibit nonlinear relationships between the voltage or current applied to them and the resulting voltage or current that they produce.
Nonlinear devices are commonly used in applications where signal distortion or modulation is desired, such as in frequency mixers, modulators, and demodulators.
It is important to note that many real-world systems and devices exhibit both linear and nonlinear behavior depending on the input conditions.
For example, an operational amplifier (Op-Amp) may exhibit linear behavior at low input signals, but its behavior may become nonlinear as the input signal increases beyond a certain threshold.
Understanding the linear and nonlinear behavior of devices is important in designing and analyzing electronic circuits and systems.
Difference Between Linear and Nonlinear Devices
Here are some differences between linear and nonlinear devices -
- Linear devices produce an output signal that is proportional to the input signal, while nonlinear devices produce an output signal that is not proportional to the input signal.
- Linear devices obey the principle of superposition, meaning that the output response to a sum of input signals is equal to the sum of the individual output responses. Nonlinear devices, on the other hand, do not obey the principle of superposition, meaning that the output response to a sum of input signals is not equal to the sum of the individual output responses.
- Nonlinear devices can generate harmonics, which are frequencies that are integer multiples of the input signal frequency. Linear devices do not generate harmonics.
- Nonlinear devices can cause distortion of the input signal, resulting in changes to the amplitude and shape of the output signal. Linear devices do not cause significant distortion of the input signal.
- Nonlinear devices often exhibit frequency dependence, meaning that their output response varies with the frequency of the input signal. Linear devices do not exhibit significant frequency dependence.
- Nonlinear devices often have a limited operating range, beyond which their output response becomes unpredictable or unusable. Linear devices typically have a wider operating range.