Why Can't We Use Capacitors Instead of Batteries?
The reason why capacitors cannot be used as a replacement for batteries is due to their limited energy storage duration, rapid voltage decay, and lower energy density.
Nonetheless, capacitors do serve specific tasks and have their unique applications.
This article will delve deeper into the reasons behind this limitation and explore the roles of capacitors and batteries in different scenarios.
Table of Contents
What Are Capacitors and Their Functions?
Capacitors are electronic components that store electrical energy in an electric field. They consist of two conductive plates separated by an insulating material called a dielectric.

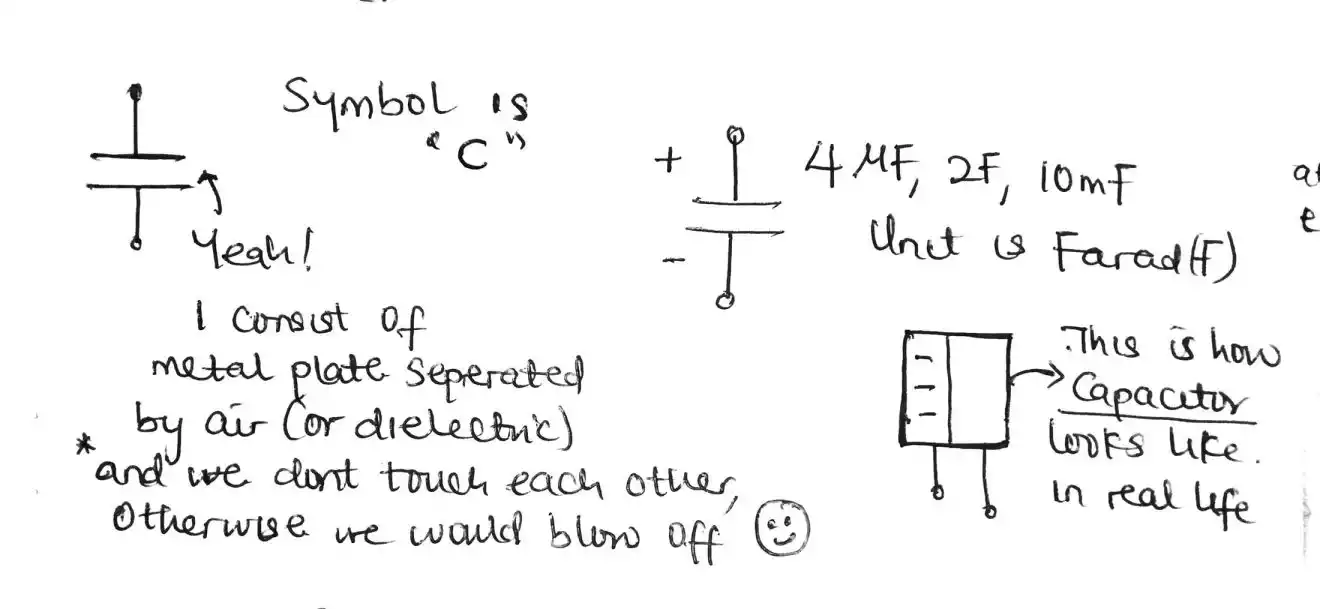
When a voltage is applied, the capacitor stores charge on its plates, and this charge can be released when needed.
Capacitors are commonly used in electronic circuits for filtering, coupling, and timing applications due to their ability to react quickly to changes in voltage.
Reasons Why Capacitors Cannot Replace Batteries
- Limited Energy Storage Duration: One of the primary reasons why capacitors cannot replace batteries is their limited energy storage duration.
Capacitors, especially conventional ones, suffer from leakage, which causes the stored charge to dissipate over time.
This leakage makes them impractical for long-term energy storage applications. - Voltage Decay: Capacitors exhibit a rapid voltage drop as energy is drawn from them.
This characteristic is not suitable for devices that require a steady and sustained energy supply, as seen in various electronic gadgets and electric vehicles. - Energy Density: Batteries have a significantly higher energy density compared to capacitors, meaning they can store much more energy in the same volume.
For energy-intensive applications, such as smartphones and laptops, batteries are preferred due to their ability to provide extended usage time. - Cost and Size: Capacitors suitable for storing large amounts of energy can be bulky and expensive compared to batteries.
The practicality of capacitors in replacing batteries diminishes when considering size and cost factors. - Discharge Characteristics: Capacitors release energy quickly in a burst, but this discharge is not always ideal for powering devices that require constant and controlled energy release.
- Self-Discharge: Capacitors tend to have a higher self-discharge rate compared to batteries.
This self-discharge can lead to energy loss and makes them less efficient for long-term storage applications. - Durable Cycles: Capacitors have a limited number of charge and discharge cycles, making them less durable than batteries, which can endure a higher number of charge cycles.
- Energy Density Measurement: The energy density of capacitors is measured in joules per cubic meter (J/m³), while batteries have a measurement of watt-hours per liter (Wh/L).
This difference in measurement reflects the much lower energy density of capacitors compared to batteries.
Capacitor Use Cases
Capacitors have their unique place in various applications due to their specific characteristics.
Some of the prominent use cases of capacitors include:
- Filtering: Capacitors are used in power supply circuits to filter out noise and unwanted voltage fluctuations.
- Coupling: They serve as coupling elements in amplifier circuits to transfer AC signals from one stage to another while blocking DC components.
- Timing: Capacitors are utilized in timing circuits, such as oscillators, to control the rate of charge and discharge, creating precise time intervals.
- Motor Starters: Capacitors are used in motor starters to provide an initial surge of energy required for starting the motor.
- Flash Photography: Capacitors are responsible for providing the sudden burst of energy needed to power the flash in photography.
Battery Use Cases
Batteries, on the other hand, are extensively used in various applications where long-term energy storage and sustained power supply are critical.

Some key use cases of batteries include:
- Portable Electronics: Batteries power smartphones, laptops, tablets, and other portable devices, providing extended usage time without constant recharging.
- Electric Vehicles: Batteries serve as the primary energy storage solution in electric vehicles, allowing them to travel long distances on a single charge.
- Renewable Energy Storage: Batteries are essential for storing excess energy generated from renewable sources like solar and wind, ensuring a consistent energy supply when the sources are not active.
- Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS): Batteries in UPS systems provide backup power during power outages, ensuring critical systems continue to operate smoothly.
- Remote Devices: Batteries power various remote devices, such as sensors and surveillance cameras, where continuous power supply through conventional means is not feasible.
Capacitors and Batteries Working Together
Capacitors can still find a place alongside batteries in certain applications. For instance, in hybrid electric vehicles, capacitors can provide a burst of power during acceleration, supplementing the energy from the battery.
This combined approach leverages the quick discharge and recharge capabilities of capacitors while relying on the long-term energy storage capabilities of batteries.
What about Super Capacitors or Ultra Capacitors?
Now you might ask what about super capacitors, why can’t they be used instead of a battery?
Super capacitors, sometimes referred to as ultra-capacitors, are advanced versions of conventional capacitors with higher energy storage capabilities.
While they can store more energy than traditional capacitors, they still face significant downsides when compared to batteries.
Wrap Up
As a wrap up, capacitors cannot replace batteries in most energy storage applications due to their limitations in long-term energy storage and voltage decay.
However, capacitors excel in specific tasks, such as filtering, coupling, and timing applications.
Meanwhile, batteries remain essential for providing sustained power supply in portable electronics, electric vehicles, and renewable energy storage.
As technology continues to advance, the combination of capacitors and batteries may offer even more efficient energy storage solutions for various industries.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
- Can capacitors store energy indefinitely? No, capacitors cannot store energy indefinitely due to leakage, which causes the stored charge to dissipate over time.
- Why are batteries preferred over capacitors for electric vehicles? Batteries offer higher energy density and longer discharge durations, making them more suitable for providing sustained power to electric vehicles during long journeys.
- Can super capacitors fully replace batteries in all applications? While super capacitors have higher energy storage capabilities than conventional capacitors, they still face limitations in terms of energy density and cost, making them unsuitable for all battery applications.
- Do capacitors require maintenance like batteries? Capacitors generally require less maintenance than batteries due to their simple structure and absence of chemical reactions. However, they still need periodic checks for leakage and proper functioning.
- Are there any advancements being made to improve capacitor technology? Researchers are continually working on improving capacitor technology to increase energy storage capacity and reduce leakage, making them more practical for certain applications.
- Can capacitors be used in combination with batteries for specific purposes? Yes, capacitors and batteries can complement each other in certain applications. Capacitors can be used to provide quick bursts of energy, while batteries handle sustained power supply.