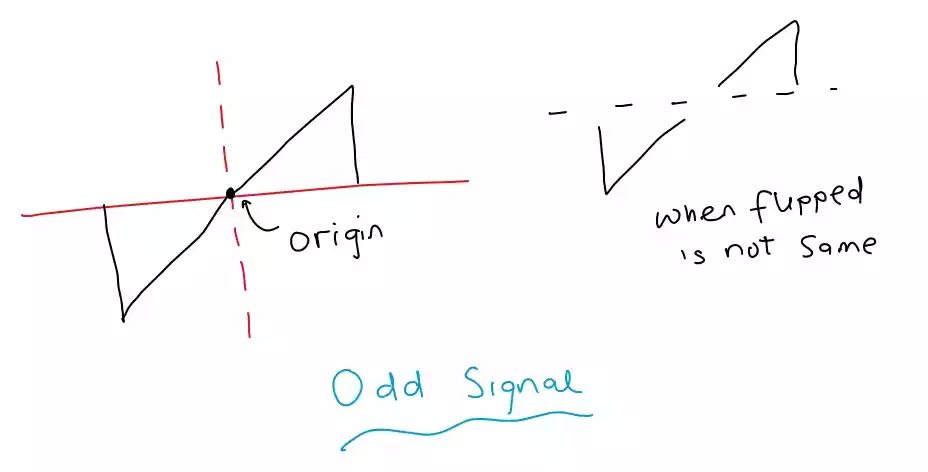
What are Dirichlet conditions for existence of Fourier series?
It is said that periodic signals can be analyzed using Fourier series, while non-periodic signals can be analyzed using Fourier transform.
But not all periodic signals will have a Fourier series expansion, hence here must be conditions a periodic signal have to meet for Fourier series to be used.
These conditions are defined by the mathematician Dirichlet, hence it is named Dirichlet conditions or the conditions for existence of Fourier series.
There are three Dirichlet conditions, which are;
Condition 1:
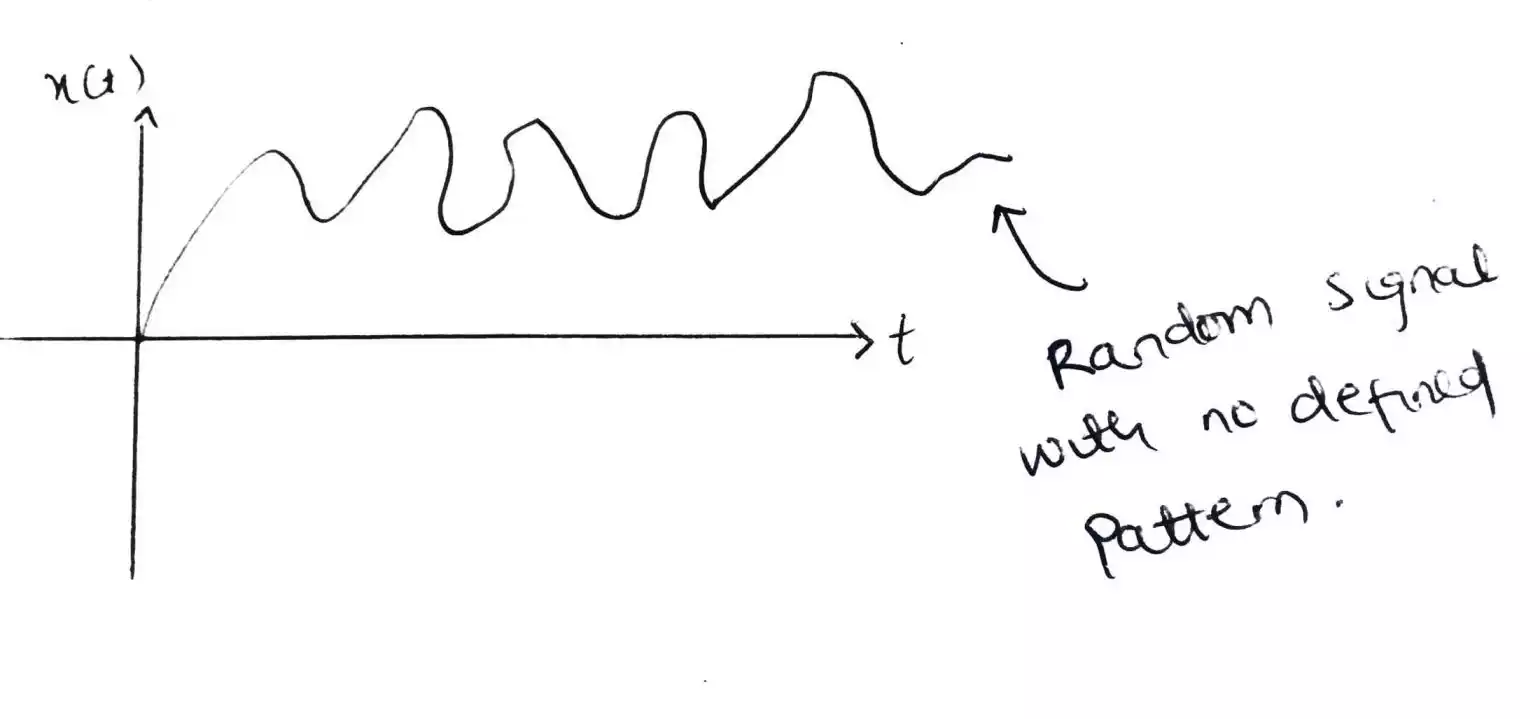
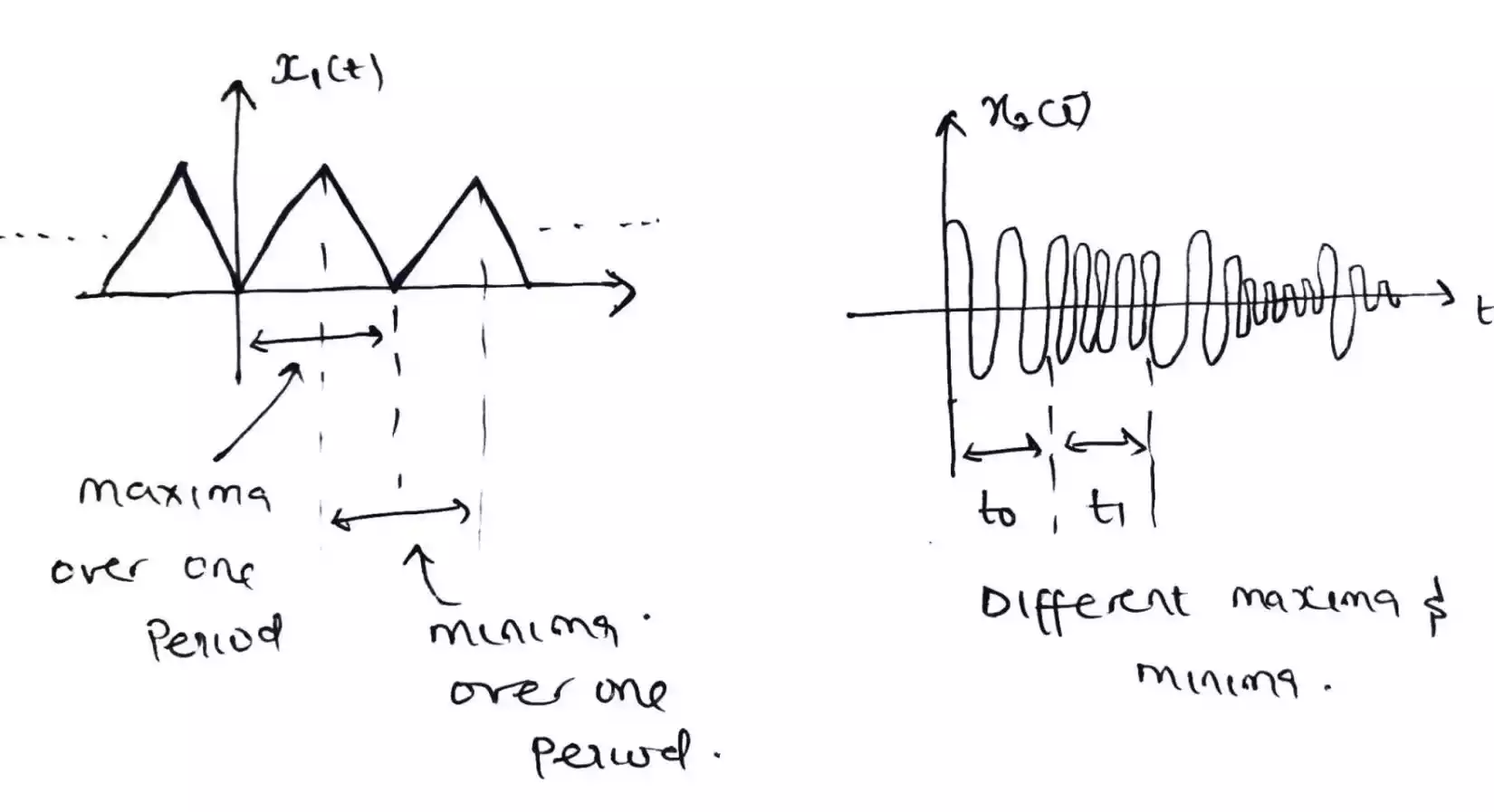
For a periodic signal to have Fourier series expansion, the signal should have a finite number of maxima and finite number of minima over the range of time period.
Maxima is the highest amplitude or peak and minima is the lowest amplitude or peak value and as you can see for each time interval, there is finite number which you can count intuitively.
In the second figure, it can be seen that the maxima and minima are not constant, and the time period has some inconsistency, hence the signal is discontinuous or infinite.
Condition 2:
A periodic signal should have a finite number of discontinuities over the range of time period. The discontinuities are the high to low or low to high transition.
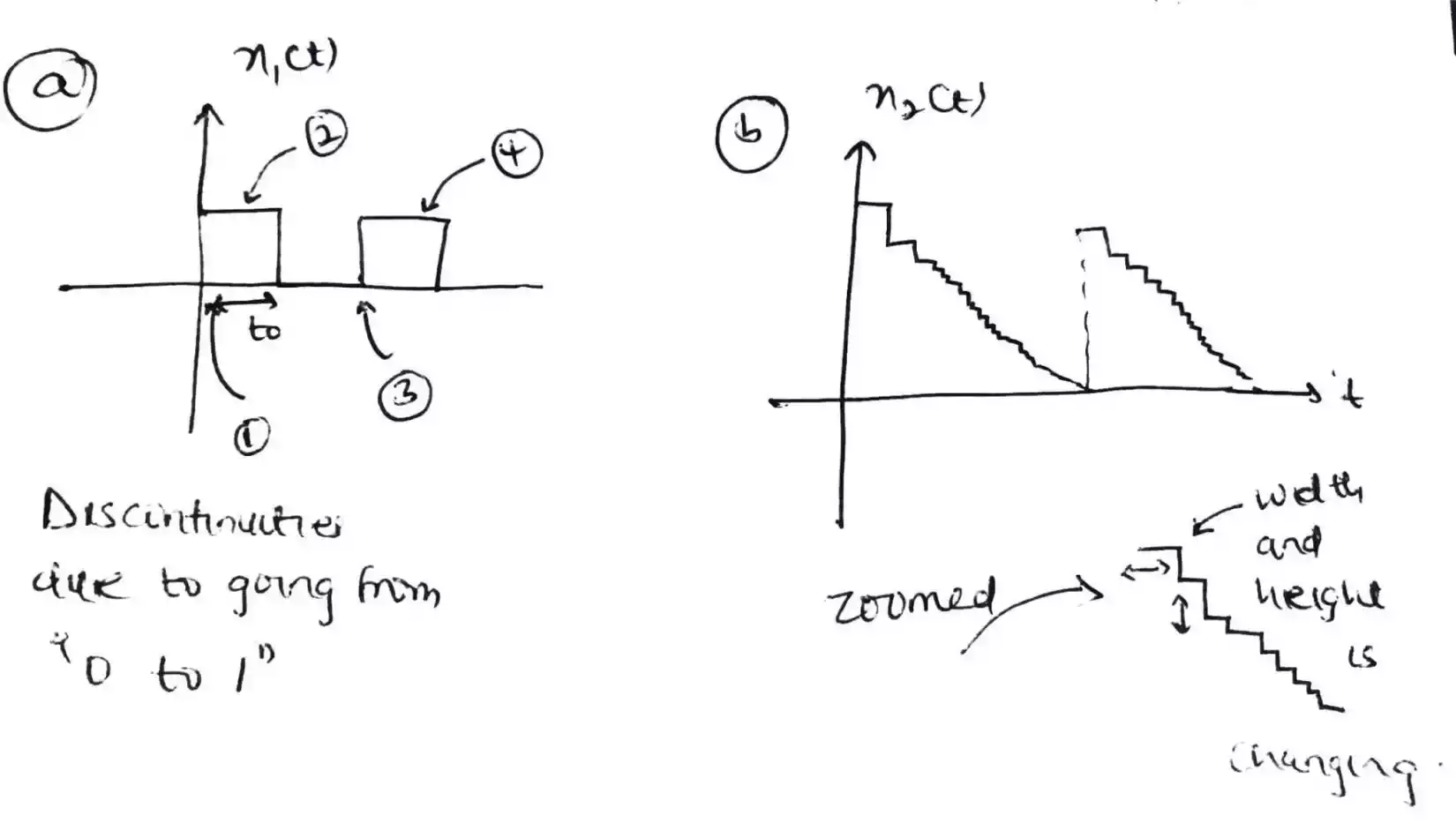
In the first figure there are finite discontinuities while in the second figure there are infinite discontinuities as the width and height is changing randomly and the discontinuities present can tend to infinity.
Condition 3:
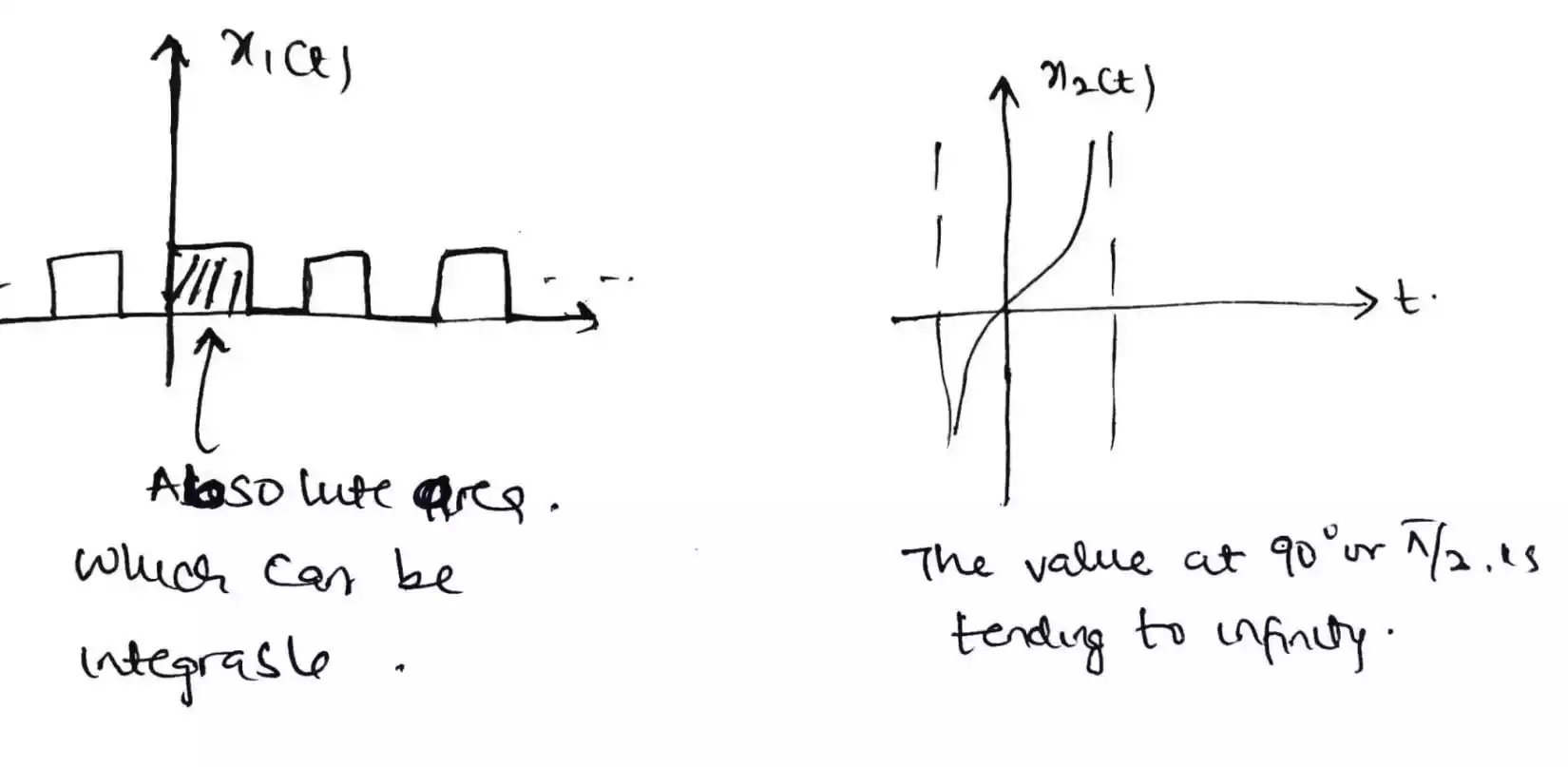
Periodic signal should be absolutely integrable over the range of time period.