What are Deterministic and Random Signals? with Examples and Differences
Signals are all around us, carrying information in various forms. A signal is a function that carries information about a physical phenomenon.
It varies with an independent variable, such as space, time, or density.
In essence, anything that conveys information can be considered a signal. Examples include: temperature of a room, voltage, and current in an electronic circuit, digital images, video, or audio etc.
We can broadly categorize signals into two types: deterministic and random signals.
Table of Contents
What are Deterministic Signals?
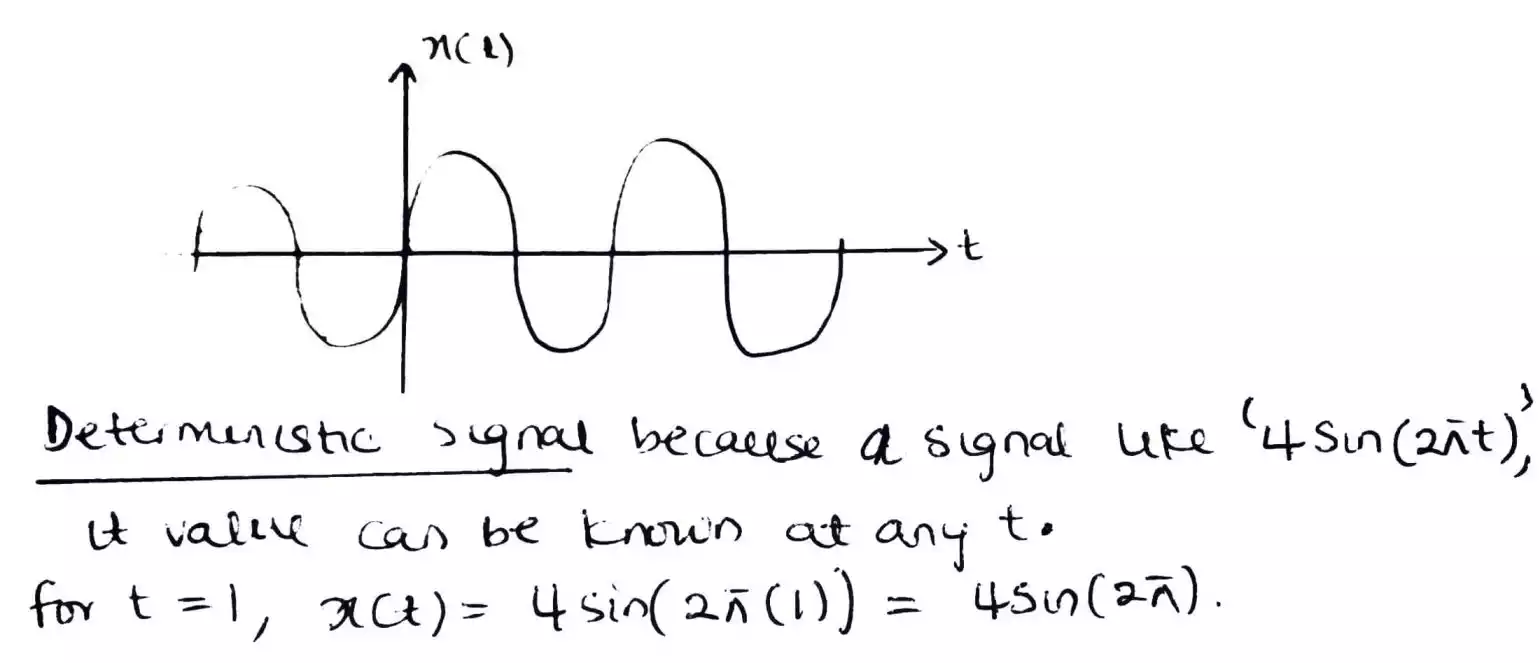
Deterministic signals are those that can be completely predicted and described by a mathematical equation or rule. They have a fixed pattern and behave consistently over time.
💡
Another definition is, a deterministic signal is a signal that has no uncertainty with respect to its value at any instant of time.
This is quite similar to Sine, since at any instant of time (t) there is a corresponding or defined value for the signal.
What are Random Signals?
Random signals also known as non-deterministic signals, on the other hand, are unpredictable and exhibit randomness in their values.
They cannot be precisely described by a single equation but are characterized by their statistical properties like mean, variance, and probability distribution.
.webp)
💡
Another definition is, a random signal is a signal that has uncertainty with respect to its value at any instant of time. It is defined in probabilistic terms, as there is no define value.
Differences between Deterministic and Random Signals
| Deterministic Signals | Random Signals | |
|---|---|---|
| Predictability | Completely predictable | Unpredictable |
| Description | Defined by a mathematical equation or rule | Characterized by statistical properties |
| Pattern | Fixed and consistent | Random and irregular |
| Examples | Sine wave, square wave, music signal (when played repeatedly) | Noise, thermal fluctuations, ECG signal |
Examples of deterministic signals:
-
Sine wave: A fundamental waveform with a smooth, periodic oscillation.
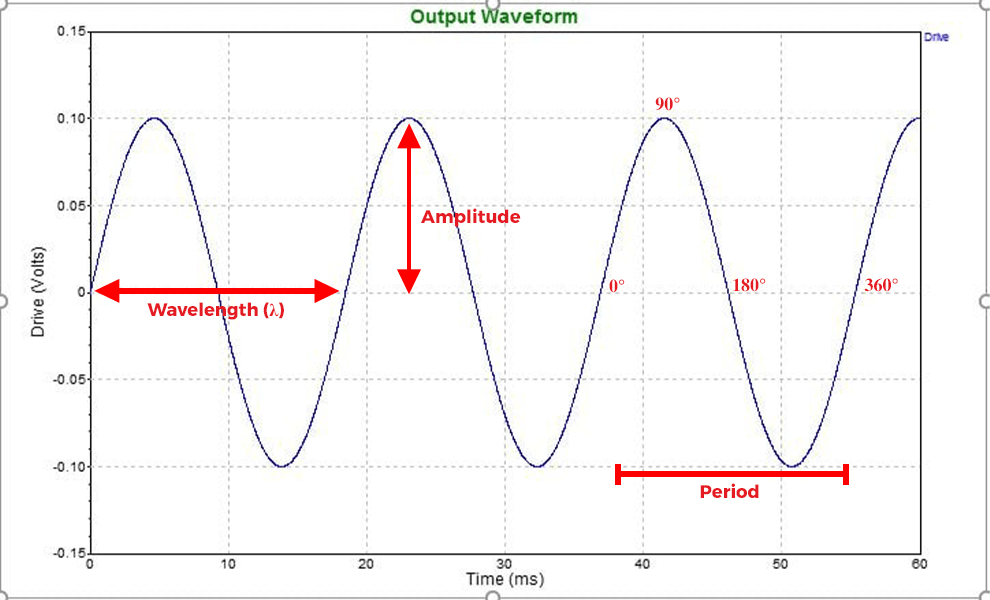
Sine Wave - Credit: VibrationResearch
-
Square wave: A periodic signal with abrupt transitions between high and low values.

Square wave and other waves - Credit: Wikipedia
-
Music signal: When played repeatedly, the music follows a specific pattern and can be precisely reproduced.
Examples of random signals:
-
Noise: Unwanted electrical or acoustic signals with unpredictable fluctuations.

White Noise - Credit: Wikipedia
-
Thermal fluctuations: Tiny, random variations in temperature due to the movement of atoms and molecules.
-
ECG signal: The electrical activity of the heart, exhibiting some randomness due to biological variations.
ECG stands for Electrocardiogram. It is a medical test that measures the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time.
Wrap Up
As a wrap up, understanding the nature of deterministic and random signals is essential for various applications.
For example, in communication systems, we aim to transmit deterministic signals (like information data) while minimizing the impact of random noise.
In medical diagnosis, analyzing random signals like the ECG can reveal valuable insights about a patient’s health.
FAQs
1. Why is the predictability of signals crucial in communication systems?
The predictability of signals in communication systems ensures the accurate transmission of information while reducing the impact of random noise.
2. How do deterministic signals differ from random signals in terms of patterns?
Deterministic signals exhibit fixed and consistent patterns, while random signals dance to an irregular beat, lacking fixed patterns.
3. Can you provide real-world examples where the understanding of random signals is vital?
Understanding random signals is important in medical diagnosis, especially in analyzing signals like the ECG to gain insights into a patient’s health.