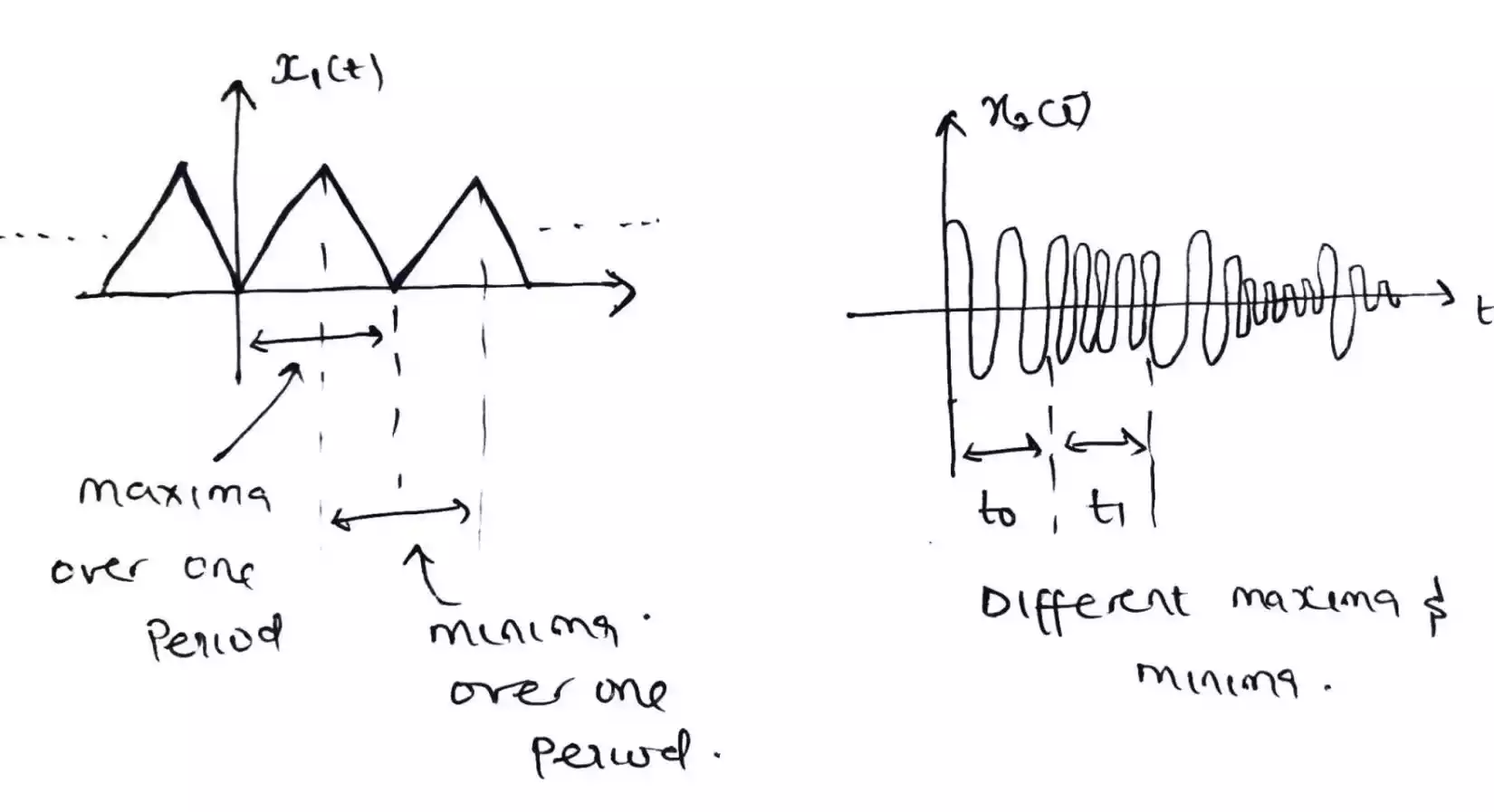
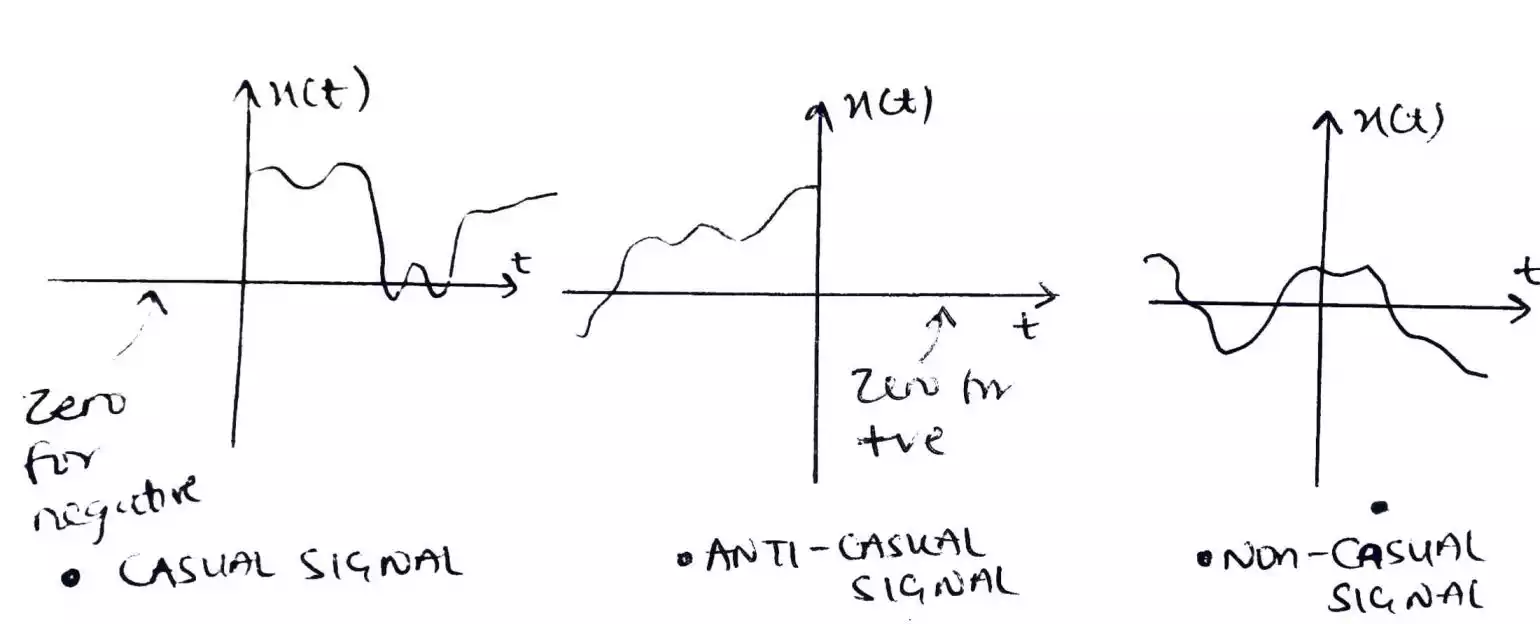
How to Determine if a Signal Is Even or Odd?
Knowing if a signal is an even or an odd signal is very important because it helps to simplify calculations and reduce the number of terms that need to be considered in a Fourier series or Fourier transform.
For example, when trying to find the Fourier analysis of a function, there are variables that need to be calculated, a0, an and bn where a0 is a constant value, an is the value associated with the even terms and bn is the value associated with the odd terms.
Now if the signal is known to be even then, there is no need for finding bn as it is the value associated with odd terms hence, bn will be zero which will make the odd terms also zero.
What is an Even Signal?
An even signal is a signal which is symmetrical about the Y-axis or vertical axis, In other words, if you reflect the signal across the vertical axis, it will look exactly the same.
For example, in the waveform or signal drawn below you can see that if you wrap the signal vertically, the part on the negative or left side is exactly the same as that on the positive or right side.
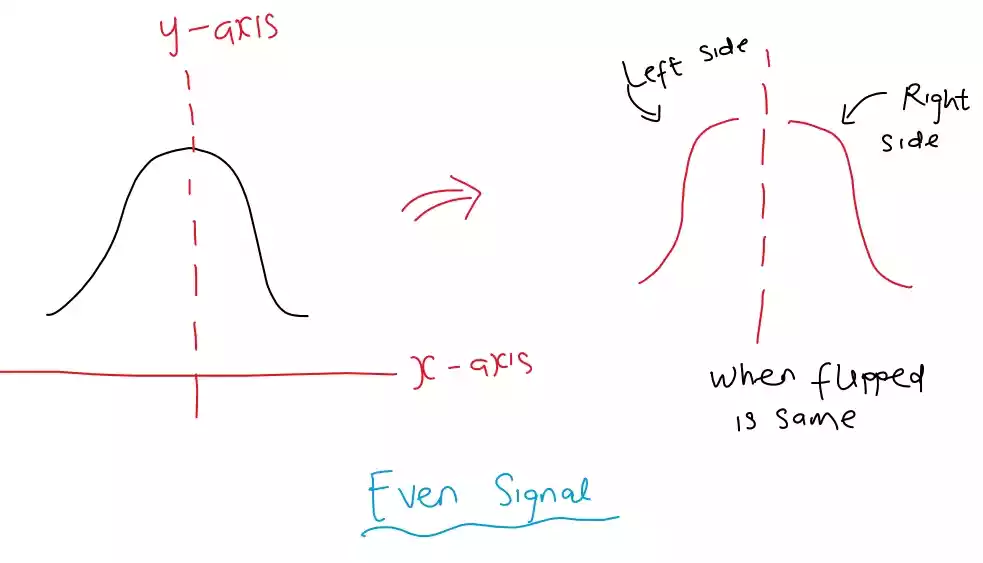
Mathematically, this can be expressed as f(-x) = f(x), where f(x) is the signal. In terms of their Fourier transform, even signals have only cosine (even) terms just as we stated earlier, which means that they do not contain any sine (odd) terms. Even signals also have an even power spectrum.
Examples of even signals include signals that represent an even function, such as a sine wave with an even period, a cosine function etc.
What is an Odd Signal?
An odd signal is a signal which is symmetrical about the origin or about the (Y-axis and X-axis), which means that if you reflect the signal across the origin, it will look exactly the same, but flipped vertically.
Here is a waveform that depicts an odd signal.
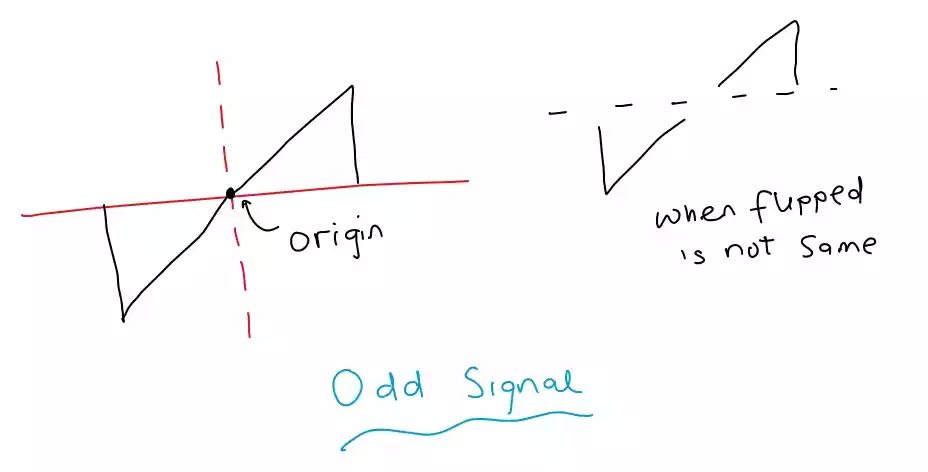
Mathematically, this can be expressed as f(-x) = -f(x), where f(x) is the signal. In terms of their Fourier transform, odd signals have only sine terms, which means that they do not contain any cosine terms. Odd signals also have an odd power spectrum.
Examples of odd signals include signals that represent an odd function, such as a sine wave with an odd period.
How to determine if a Signal Is Even or Odd?
To determine if a signal is even or odd, when you are given a function f(x) just substitute “-x” into the function f(x) which will result in f(-x). If f(-x) (the new function) is equal to the original function f(x) i.e., f(-x) = f(x) then, it is an even signal.
But if f(-x) is equal to the negative version of the original function f(x) i.e f(-x) = -f(x) then, it is an odd signal.
Let see some examples;
-
Given that f(x) = -3x2 + 4, determine if it is even or odd.
Substitute wherever x is to be -x therefore we have f(-x) = -3(-x)2 + 4.
A further simplification, f(-x) = -3(x)2 + 4 as the square of any negative number results in a positive number.
Since f(x) = -3x2 + 4 and f(-x) = -3(x)2 + 4 it can be seen that both f(x) and f(-x) has the same value therefore f(x) = f(-x) which makes the function an even function.
Other examples of an even function is cos(x), cosh(x), x2 etc. -
Given that f(x) = 7x3 – 3x, determine if it is even or odd.
By applying the steps as above, f(-x) = 7(-x)3 – 3(-x).
So f(-x) = -7x3 + 3x as the cube of any negative number yields a negative number also the multiplication of a negative sign and another negative sign give s a positive sign.
By comparing f(x) = 7x3 – 3x and f(-x) = -7x3 + 3x, as f(-x) is not equal to f(x) then it is considered to be an odd function.
Note: You can see that f(-x) = -7x3 + 3x can be written as -f(x) just by factorizing f(-x). i.e., f(-x) = -f(x) = -(7x3 - 3x).
Other examples of an odd function is sin(x), x3 etc.