Why Is Laser Used in Optical Fiber Communication?

Optical fiber communication is a method of transmitting information over long distances using optical fibers, which are thin, flexible, and transparent cables made of glass or plastic.
Read on: Why Optical Fiber Communication Is Preferred Over Other Means of Communication?
These fibers are capable of transmitting light signals over long distances with minimal signal loss or attenuation, making them an ideal medium for high-speed communication or data transmission.
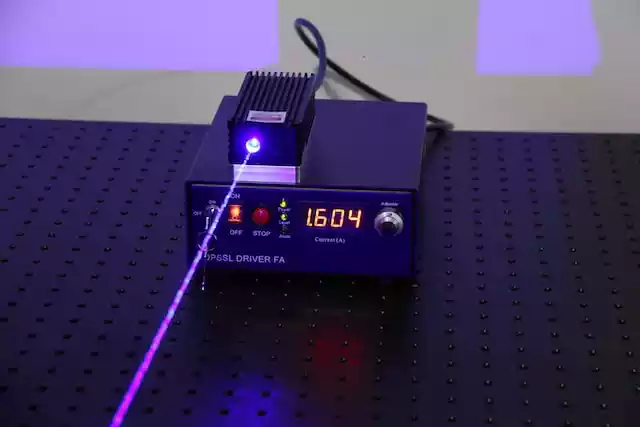
In order to transmit information over an optical fiber, a light source is needed to generate the optical signal. This light source must be able to produce a coherent beam of light, which means that the light waves are in phase with each other and have a constant amplitude and frequency.
A laser is an ideal light source for this purpose, as it produces a highly coherent beam of light that can be easily modulated to carry information.
Read on: LASER and its Characteristics
Why Is Laser Used in Optical Fiber Communication?
Laser is used in optical fiber communication because, it can produce a very high intensity, coherent beam of light that can carry a large amount of information over long distances with minimal signal loss or attenuation.
The light produced by a laser is monochromatic (meaning, it is of a single wavelength) and is tightly focused into a narrow beam, which allows it to travel through the optical fiber with very little dispersion or attenuation.
Laser light is produced by a process called stimulated emission. In this process, photons (particles of light) are emitted from an excited atom or molecule when they are hit by another photon with the same energy and frequency. This creates a cascade of photons that are all in phase with each other, creating a highly coherent beam of light.
Read on: Optical Sources in Optical Fiber Communication
In an optical fiber communication system, the laser light is modulated with the information that needs to be transmitted. This can be done by varying the intensity, frequency, or phase of the light in accordance with the data being transmitted.
For example, in a digital communication system, the laser can be turned on and off rapidly to represent binary 1s and 0s.
The modulated laser light is then coupled into the optical fiber, which guides the light signal to the receiver at the other end of the fiber. The light signal travels through the fiber by repeatedly bouncing off the walls of the fiber core, a phenomenon known as total internal reflection (TIR).
Read on: What Is Fiber Optics Cable, Modes of Propagation and How Does Light Travels Through It
The fiber is coated with a cladding material that has a lower refractive index than the core, which helps to confine the light within the core and minimize loss due to scattering or absorption.
At the receiver end of the fiber, the light signal is detected and converted back into an electrical signal by a photodetector. The electrical signal can then be processed by electronic circuitry to recover the original data.