What Is Fiber Optics Cable, Modes of Propagation and How Does Light Travels Through It
There are several guided medium which are used for the transmission of data e.g. coaxial cable and fiber optics cable. But fiber optics cable provides better advantage to coaxial cable as it uses light as optical source while coaxial cable uses electric signal.
What is fiber optics cable?
Fiber optics cable is a dielectric (or insulated) material (e.g. glass) which is used to transmit light pulses or optical signal. The optical sources are mostly LASER or LED.
How does light travels through an optical fiber?
In order to understand how light travels through an optical fiber, the basics of how light changes from one medium to another need to be considered.
Light travels in a straight line as long as there is no obstacle or interference which will cause it to change direction or bend.
But when light travels from a denser medium (e.g. inside a dielectric) to a rarer medium (e.g. air) and vice versa, the angle at which the light ray enters the first medium is difference from the angle at which it goes out to the other medium.
Looking at the sketch below, when the angle of incidence in less than the critical angle then refraction occurs and it has an angle greater than the angle of incidence. But when the angle of incident is equal to critical angle then the angle of refraction is 90degree of parallel to the boundary.
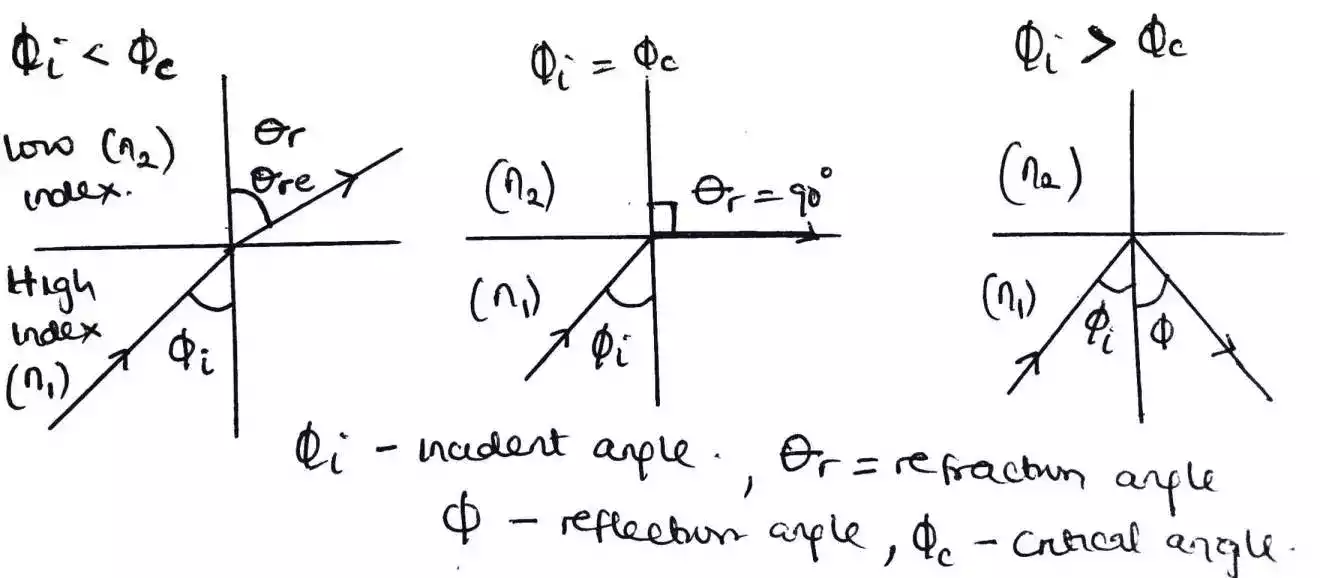
However, if the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle then internal reflection occurs. This internal reflection or total internal reflection (TIR) is what make light to travel through an optical fiber.
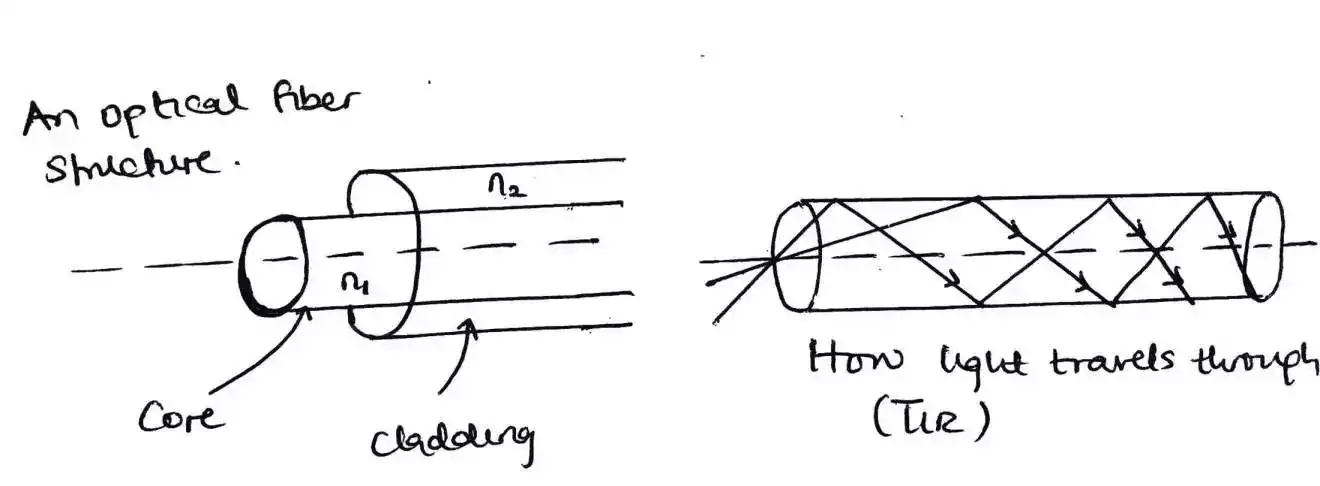
But in order to make these two mediums in an optical fiber then, a core and cladding is used and a coating for insulation.
The core of a fiber is where the light rays travel enters while the cladding which surround the core is another medium. The core is very thin and light and it is said to have an approximate width close to a hair strand.
The core which is denser has a refractive index greater than the refractive index of the cladding.
Propagation modes in optical fiber.
Generally, there are two types of modes that support propagation of light along an optical fiber. Each of the modes has different physical characteristics.
-
Single mode fiber
-
Multimode fiber
- Step index fiber and
- Graded index fiber
As it is seen, there is single mode and multimode. The multimode is further then classified as step index and graded index fiber.
Single mode fiber
as the name implies, allow one light ray to travel through it. It is simple, has small diameter and leads to less dispersion as compared to multimode which is discussed below.
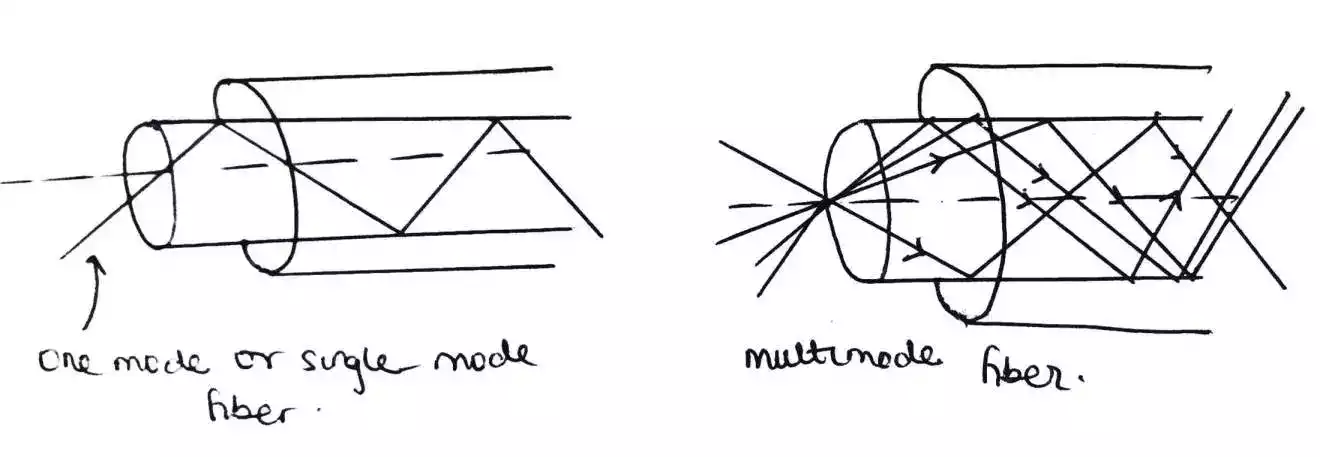
Multimode fiber
In multimode, as the name implies allow several modes or many light rays to travel through it. The different light rays travel through the fiber at different angle. The angle limit at which light rays can travel is termed as the acceptance angle.
Multimode fiber has wider core diameter.
Multimode step index fiber
In a step index fiber, the refractive index of the core-cladding interface is relatively constant. In essence, no gradual change in the refractive index at the core-cladding interface and this results in a step change and the light is reflected back.
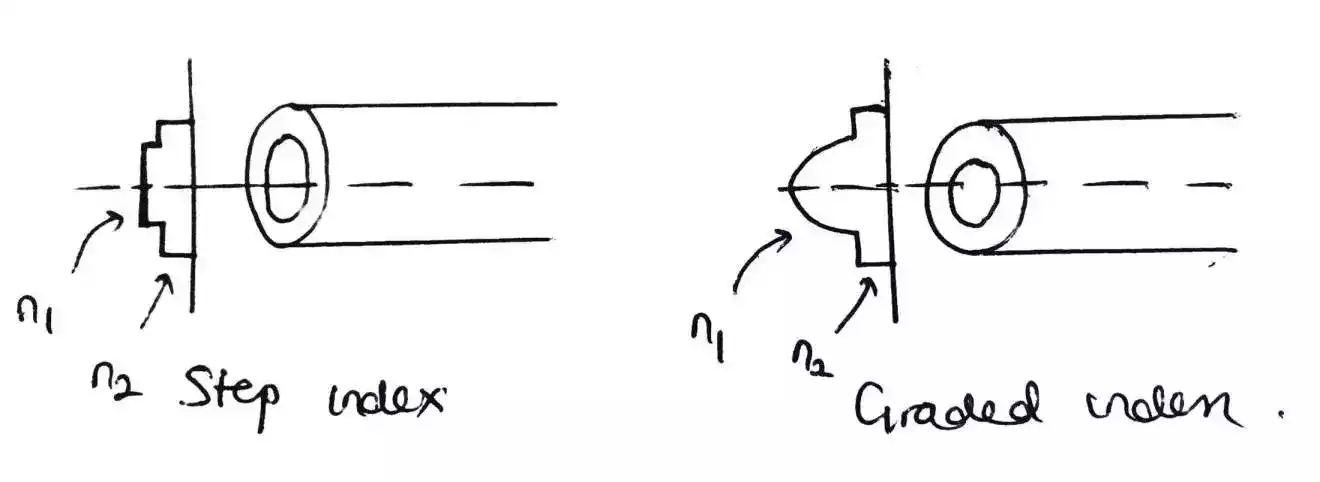
Multimode graded index fiber
In grade index fiber, there is gradual change in refractive index hence, reflection of light is not as in step index.
Summary
An optical fiber is used for transmitting signal or light pulses (e.g. from Laser or LED) over a long distance.
Light travel through an optical fiber due to total internal reflection.
Optical fiber consists of a core, cladding and coating. Light rays enters through the core and the cladding is used for causing refraction and reflection while the coating is a protective insulator.
The number of light that can travel through an optical fiber depends upon the type of fiber used.
A single mode fiber can allow only one light ray to travel through it while a multimode fiber can allow several of light rays to travel through it.
The multimode is also divided based on the core-cladding refractive index changes. As a step index or graded index fiber.
A step index fiber is one with constant core and relatively less cladding refractive index while a grade index fiber core-cladding refractive index is not constant.





