What Is ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) in Networking?
ARP is a protocol which allow computers or hosts to work on layer 2 (Data link Layer) with a known IP address.
What is ARP in networking?
ARP stands for address resolution protocol. It is an internet protocol in networking designed to discover a MAC address and then map it to an IP address.
How does ARP works in networking?
Let’s use the figure below which shows four computers that are connected to a switch to form a local network.
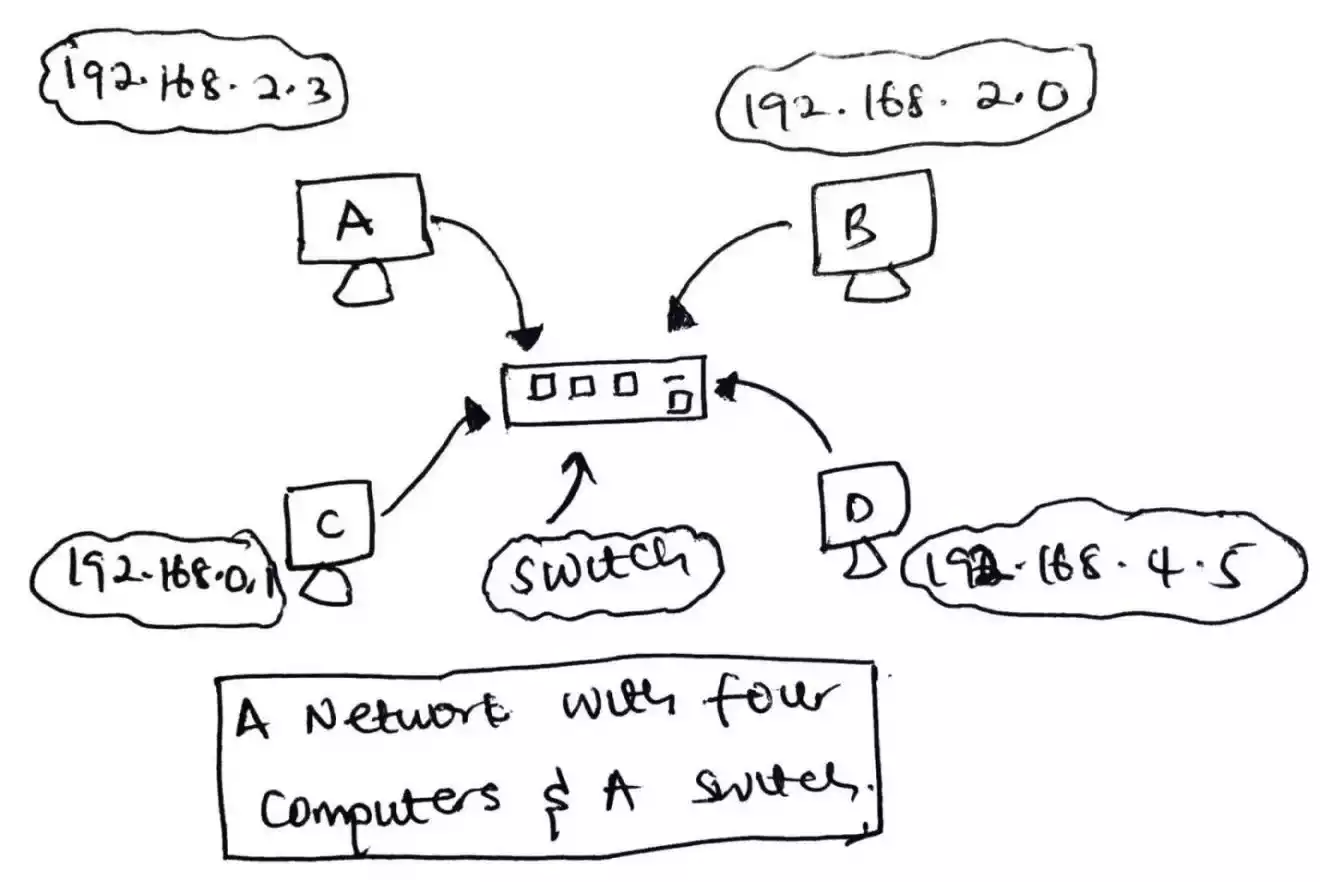
If computer A wants to communicate with computer C given that the IP address of computer C is known, computer A cannot just send packets to C using C’s IP address because a switch which the computers are connected to is a layer 2 device (Data Link Layer) which uses a MAC address (also called physical address).
In that case, if computer A wants to communicate with C, it needs it MAC address instead of the known IP address and in order to get the MAC address of computer C, computer A sends a broadcast message across the network and the switch directs the message to computer B, C and D.
Computer B and D will discard the message as it is not for them but C will say hey! That’s my IP address.
After computer C received the broadcast message and acknowledged it, it will reply with its MAC address.
If computer A receives the MAC address of C, it stores it on a table called ARP cache. The ARP cache is a table that associate the known IP or internet address (e.g. 198.162.4.4) with the corresponding MAC address (e.g. 10-22-AE-45-5E-01).
Since, computer A has the MAC address of C now, it will use the MAC address to communicate with computer A and the reason it stores it on the ARP cache is for further communication so instead of sending a broadcast message again, it just looks on it ARP cache and access the matching MAC address.
The Arp cache look something like this;
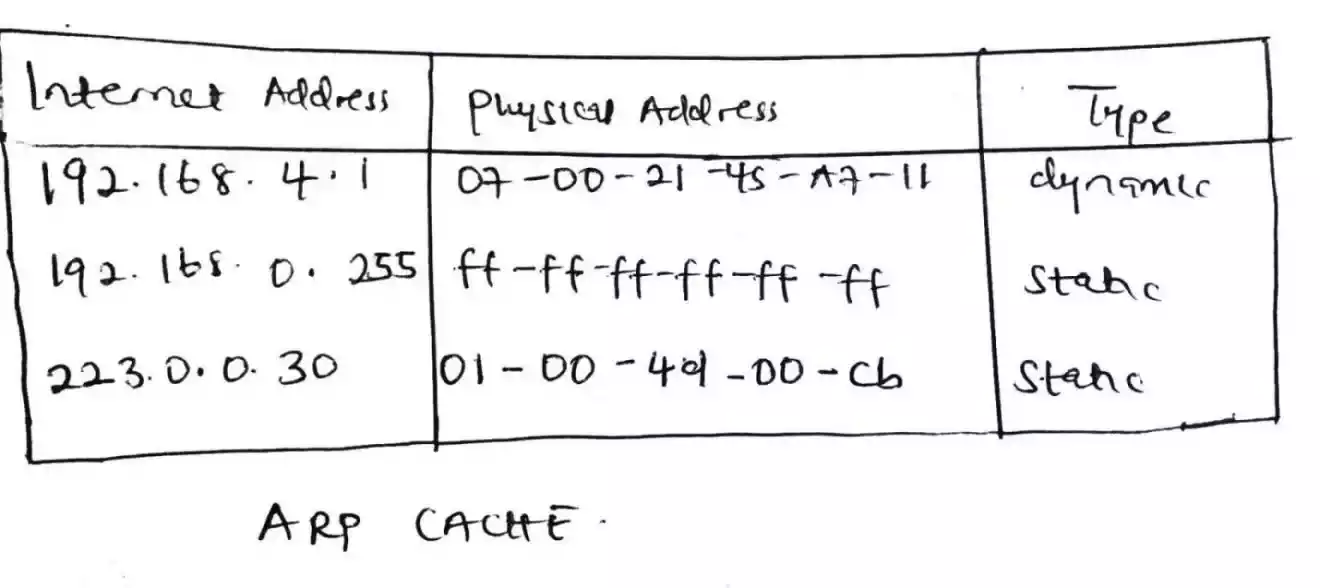
It has an “Internet Address” column which consists of list of the IP addresses.
The second column is the “Physical address” and it store the corresponding MAC addresses as we state earlier
and lastly is the “Type column” and it tells if the MAC address associated to an IP address is typed statically or is dynamically store.