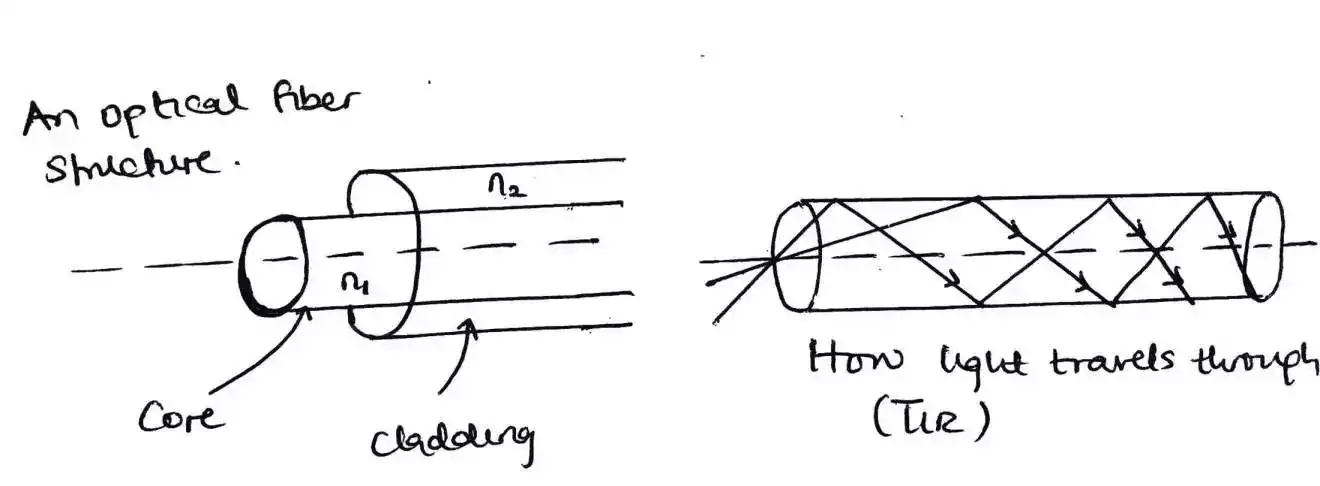
Differences Between Step-Index and Graded-Index Optical Fiber
Fiber optics has revolutionized the way we transmit information over long distances. Optical fibers are used to transmit light signals over long distances with minimal signal loss.
These fibers come in two main types: step-index and graded-index optical fibers.
One of the major difference between a step index fiber and a graded index fiber is that,
A step index fiber has a core with constant refractive index and make a step change from the core – cladding interface.
Whilea graded index fiber does not have a core with constant refractive index, and it makes a gradual change from the core – cladding interface.
In this blog post, we will explain the differences between these two types of optical fibers.
What is a step-index fiber?
Step-index optical fiber is the most common type of optical fiber. It consists of a core made of a single material, surrounded by cladding material of lower refractive index.
The core and cladding have different refractive indices, which causes light to be reflected back into the core when it reaches the interface between the core and cladding.
This allows the light to be transmitted along the fiber with minimal signal loss. The refractive index of the core is usually higher than that of the cladding.
The diameter of the core can vary depending on the application, but is typically around 10 micrometers. The cladding is usually made of a material with a lower refractive index, such as silica.
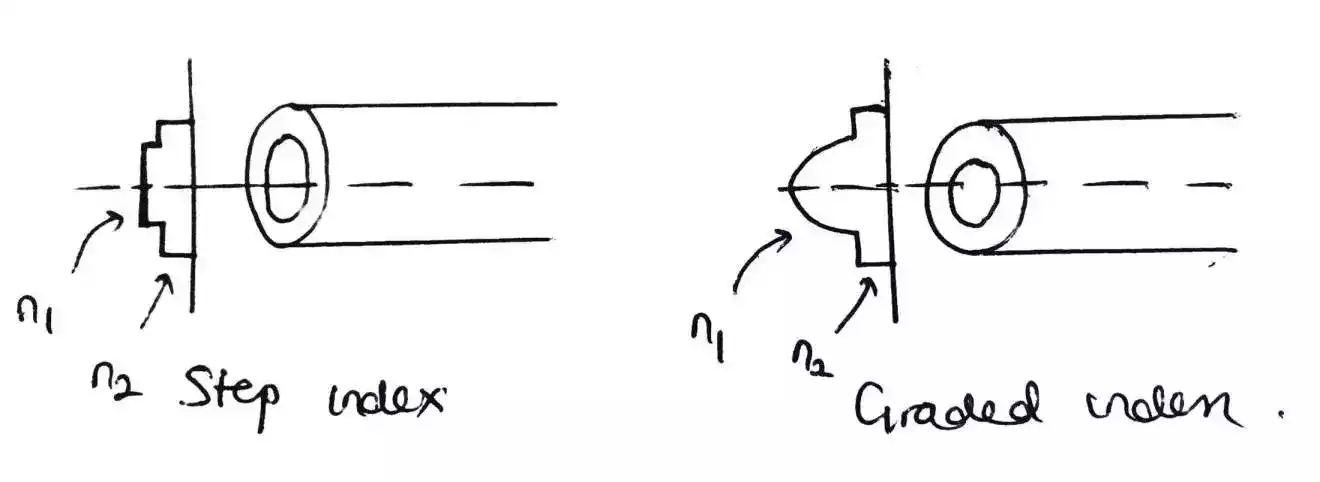
What is a graded-index fiber?
Graded-index optical fiber is a type of optical fiber that has a continuously varying refractive index profile from the center of the fiber to the edge (in a gradual process).
The core of the fiber is made of a material with a high refractive index, which gradually decreases towards the edge of the core.
This creates a smooth transition of the refractive index, which allows the light to travel through the fiber in a curved path, minimizing modal dispersion.
The diameter of the core is typically around 50 micrometers, which is larger than the core diameter of step-index fibers.
The cladding is usually made of a material with a lower refractive index than the core, such as silica.
Difference Between Step-index and Graded-index Fiber in Tabular Form
| s/n | Step Index Fiber | Graded Index Fiber | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Refractive Index | It has a constant core refractive index | It does not have a constant core refractive index |
| 2 | Index Profile | The refractive index profile makes a step change at the core-cladding interface | The refractive index profile makes a gradual change at the core-cladding interface |
| 3 | Mode | Step index occur in single mode fiber and multimode fiber | Graded index occur in multimode mode fiber only |
| 4 | Propagation Path | Light propagates in step index fiber in a zigzag form | light rays propagates in a skew or helical form |
| 5 | Dispersion | Step index fibers have higher dispersion | Graded index fibers have lower dispersion |
| 6 | Cost | Step index fibers are simple and less expensive to manufacture | Graded index fibers are more expensive to manufacture |
| 7 | Numerical aperture | Step index fibers have a higher numerical aperture | Graded index fibers have a lower numerical aperture |
| 8 | Transmission Performance | Step index fibers have less transmission performance | Graded index fibers have a better transmission performance due to the lower dispersion and reduced reflection |
Step-index fiber:
- It has a constant core refractive index.
- The refractive index profile makes a step change at the core-cladding interface, as opposed to the gradual change which graded index fiber makes.
- Step index occur in single mode fiber and multimode fiber hence, they are term single-mode step index fiber and multimode step index fiber respectively.
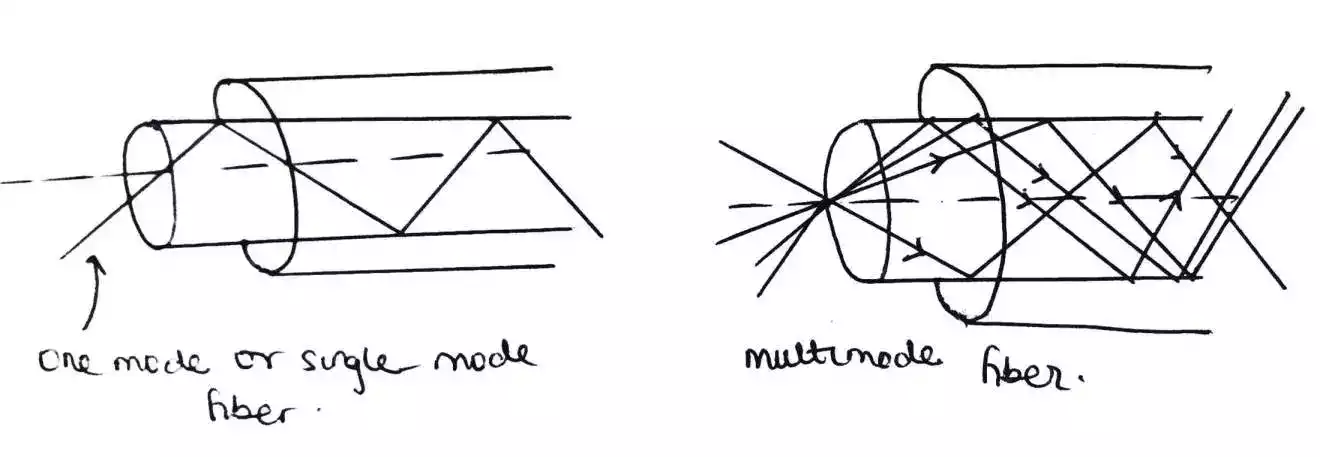
- The single mode step index fiber which is also called mono-mode step index fiber has a core diameter in the order of 2 – 10um while the multimode step index fiber has a core diameter greater than 50um (micro meter).
- Light propagates in step index fiber in a zigzag form.
- In single mode step index fiber, there is the presence of low intermodal dispersion (i.e., there is less pulse broadening) while in multimode step index fiber, because of many rays of light propagates through the fiber there is the presence of pulse broadening.
- Because of pulse broadening, multimode has low bandwidth, and it can be used in low bandwidth application, while single mode has a higher bandwidth than multimode.
- Also, due to the low bandwidth of the multimode step index fiber, it has more attenuation than that of the single-mode step index fiber.
- Step index fiber is often used for short distance communication.
- Step index fibers are less expensive to manufacture than graded index fibers.
- They have a higher numerical aperture, this allows them to collect light from a wider range of angles.
- Step index fibers have higher dispersion.
- They have less transmission performance due to dispersion and reflection.
Graded-index fiber
- It does not have a constant core refractive index.
- The refractive index profile makes a gradual change at the core-cladding interface as opposed to a step change which step index fiber makes.
- Graded index occur in multimode mode fiber only.
- The light rays that propagates in a graded index fiber is either in a skew or helical form.
- Graded index fiber has a higher bandwidth.
- There is less attenuation of light rays.
- Graded index fiber is typically used for long distance communication.
- They are more expensive to manufacture.
- Graded index fibers have a lower numerical aperture.
- They have lower dispersion.
- Due to the lower dispersion in graded index fiber and the reduced reflection at the core-cladding interface, It has a better transmission performance.