Why Hexagonal Shape Is Preferred in Cellular Architecture?
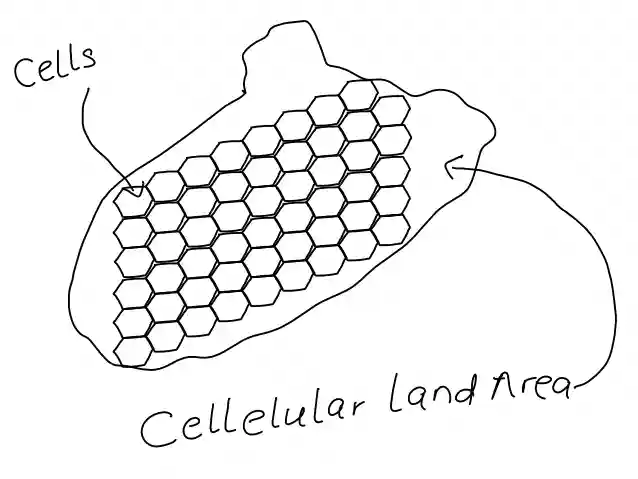
A cellular land area in cellular networks refers to the geographical area that is divided into smaller regions, or cells, each of which is served by a mobile phone base station.
The size and shape of the cells depend on factors such as the number of users in the area, the terrain, and the availability of resources.
The hexagonal shape is preferred in cellular architecture because, it allows for complete and balanced coverage with minimal overlap, which reduces the number of base stations required to cover an area.
The use of hexagons ensures that the cells are as close to circular as possible, minimizing interference between neighboring cells.
The use of the hexagonal shape also allows for efficient use of available resources, such as power and bandwidth, by ensuring that the base stations are evenly distributed throughout the service area.
These benefits make the hexagonal shape a preferred choice for cellular network design.
Let’s look in detail why the hexagonal shape is preferred in cellular architecture.
The geometrical shape used in a cellular network can be circular, triangular, rectangular, or hexagonal.
But in choosing the shape of the cell to be used, the following criteria are considered.
- The cell has to be geometrical.
- There should be area without overlapping.
- The area of the cell should be maximum.
The radiation of radio waves from a mobile phone base station antenna, can be approximated to be circular.
Circle as a geometrical shape has a large area and can be used to cover large regions or cells.
But the issue is that using a circular shape leads to overlapping or dead spot (which results in interference and region where signal cannot be received).
Therefore, it failed one of the criteria, which is “There should be area without overlapping”.
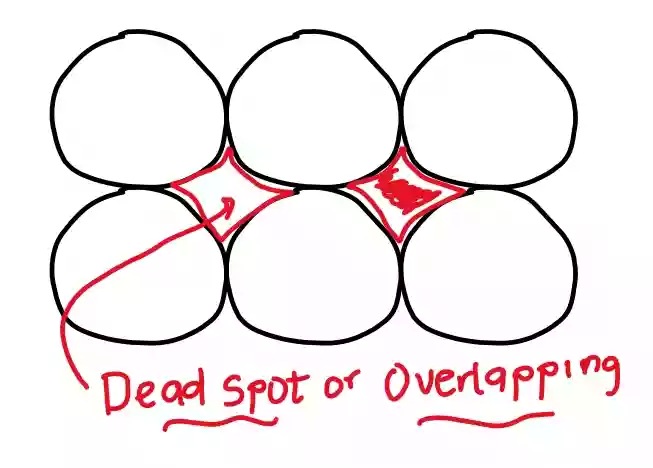
When a triangular shape is used, there is minimal to no overlapping, but the area it can cover compared to that of the circle is 17.7% of the area of the circle.
For a rectangular shape, there is minimal overlapping and the area it can cover in respect to the circle is 63.7%.
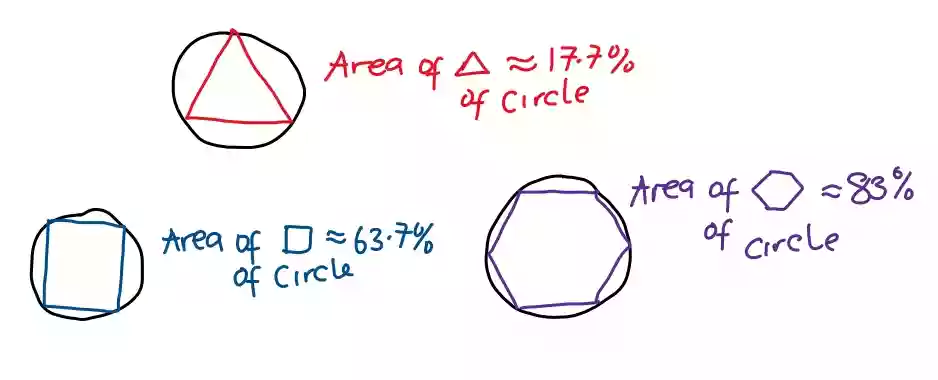
When hexagonal is used, it covers about 83% of the area of a circle and there is no overlapping.
From all the shapes, it can be seen that hexagon meet most of the criteria because of its large area.
The use of hexagons is based on the mathematical principle that hexagons are the most efficient shape for covering a two-dimensional plane with equal-sized cells, while minimizing the overlap between neighboring cells.
Why Hexagonal Shape Is Used in Cellular Network
Using hexagons in a cellular network provides a number of advantages.
- The hexagonal shape allows for complete and balanced coverage with minimal overlap, reducing the number of base stations required to cover an area.
- The use of hexagons ensures that the cells are as close to circular as possible, which helps to minimize interference between neighboring cells.
- The hexagonal shape allows for efficient use of available resources, such as power and bandwidth, by ensuring that the base stations are evenly distributed throughout the service area.