Difference Between console.log and console.error
In JavaScript programming, developers often use console.log and console.error for debugging and troubleshooting purposes.
These two functions play a vital role in displaying messages and information in the console.
In this article, we will look at these differences in detail and understand when to use each function effectively.
Table of Contents
The Purpose of console.log
The console.log function is primarily used to log general messages and information to the console.
It is commonly employed for debugging and providing insights during the development process.
Developers can use this function to print variables, objects, arrays, and strings, allowing them to examine the state of their code at different points in the program execution.
When to Use console.log
The console.log function is suitable for various scenarios, including:
- Displaying Variable Values: Use console.log to output the value of variables, enabling you to verify if they hold the expected data.
- Tracking Program Flow: By strategically placing console.log statements throughout your code, you can track the execution flow and identify potential issues.
- Debugging Complex Functions: When dealing with complex functions, logging intermediate values using console.log can help isolate the source of errors.
- Analyzing Loop Iterations: When working with loops, console.log can be used to print the values of variables within each iteration, aiding in understanding the loop’s behavior.
Example Usage of console.log
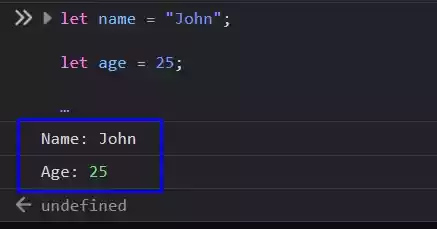
let name = "John";
let age = 25;
console.log("Name:", name);
console.log("Age:", age);
The Purpose of console.error
While console.log is used for general logging, console.error is specifically designed to highlight errors and exceptional situations.
It outputs error messages with a distinct appearance, making them more noticeable in the console.
When an error occurs, developers can utilize console.error to capture relevant details and quickly identify the problematic sections of their code.
When to Use console.error
The console.error function is particularly useful in the following scenarios:
- Error Reporting: When an error or exception is encountered, using console.error helps in generating detailed error messages, making it easier to identify the cause of the issue.
- Unreachable Code: If certain parts of your code are unreachable or conditional statements are not being met, console.error can assist in identifying these problematic areas.
- Testing and Validation: During testing and validation processes, console.error can be employed to ensure that specific conditions or code branches are executed as expected.
- Error Tracking: By logging errors with console.error, you can track the occurrence and frequency of specific errors, aiding in their resolution.
Example Usage of console.error
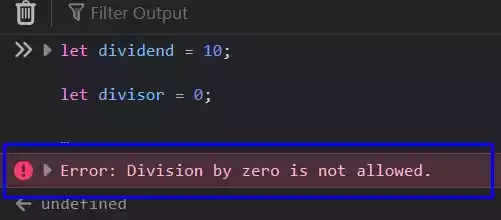
let dividend = 10;
let divisor = 0;
if (divisor === 0) {
console.error("Error: Division by zero is not allowed.");
} else {
console.log("Result:", dividend / divisor);
}
Wrap Up
Console.log and console.error are valuable tools in JavaScript development. While console.log is used for general logging and displaying information, console.error is specifically designed for highlighting errors and exceptional situations.
Having a good understanding of the differences between these two functions allows developers to effectively troubleshoot and debug their code, leading to more efficient and reliable JavaScript applications.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
- What is the difference between console.log and console.error? The main difference dwells in their purpose. console.log is used for general logging and displaying information, while console.error is specifically designed for highlighting errors and exceptional situations.
- Can console.error be used for general logging? While console.error can technically be used for general logging, it is not recommended.
Its distinctive appearance is meant to draw attention to errors, making them more noticeable in the console. - Are console.log and console.error available in all JavaScript environments? Yes, console.log and console.error are standard features of the JavaScript language and are available in most modern web browsers and development environments.
- Can I customize the appearance of console.error messages? The appearance of console.error messages is typically determined by the browser or development environment.
However, some tools and frameworks may provide options to customize the error message formatting. - Is there a performance difference between console.log and console.error? In general, the performance difference between console.log and console.error is negligible.
Both functions have minimal impact on the overall performance of the JavaScript program. - Can I use console.log and console.error in Node.js? Yes, console.log and console.error can be used in Node.js applications.
They function similarly to their browser counterparts and are useful for debugging and error reporting in server-side JavaScript code.