What Is DNS (Domain Name Server) and How It Works?
Every website can be accessed through an IP address but memorizing this addresses (written in such form 196.168.45.5) can be difficult rather, a name is given to a user in order to access the internet. The conversion or resolving of the domain name you are given to the actual IP address is a task carried out by DNS.
What is DNS?
DNS stands for Domain Name System. It is a system which is used to resolve or convert a domain name to IP address.
Because as we said earlier, with the billions of web address present on the internet today, it would not be reasonable for humans to be able to know most of these addresses (IP addresses) which points to a website or a server except if he/she is a geek.
To make life easier, DNS allow human to access website through the use of names as oppose to an IP address. It does so by taking the domain name typed in a browser e.g. tooabstractive.com, and the DNS server will search through it database and look for an IP address that corresponds to the domain name typed in.
If the server is able to locate the IP address, it resolves the domain name to it thereby, redirects or point the user to the webpage.
But this process is quite complex so let’s see how.
How does a DNS work?
If a user type in a URL such as google.com, the browser checks it cache memory (local server) to look for the IP address that link to it, and then point the user to the webpage but if it could not find the associated IP address, a query is sent to the resolver server (or ISP Internet Service Provider).
When the resolver receives the query, it would check its own cache memory to see if there is an associated IP address to the domain name you typed but, if it could not find it still, the query is further sent to the root server.
The root server basically is of 13 different types spread strategically around the globe. These root servers have their unique IP address and are operated by 12 different organizations.
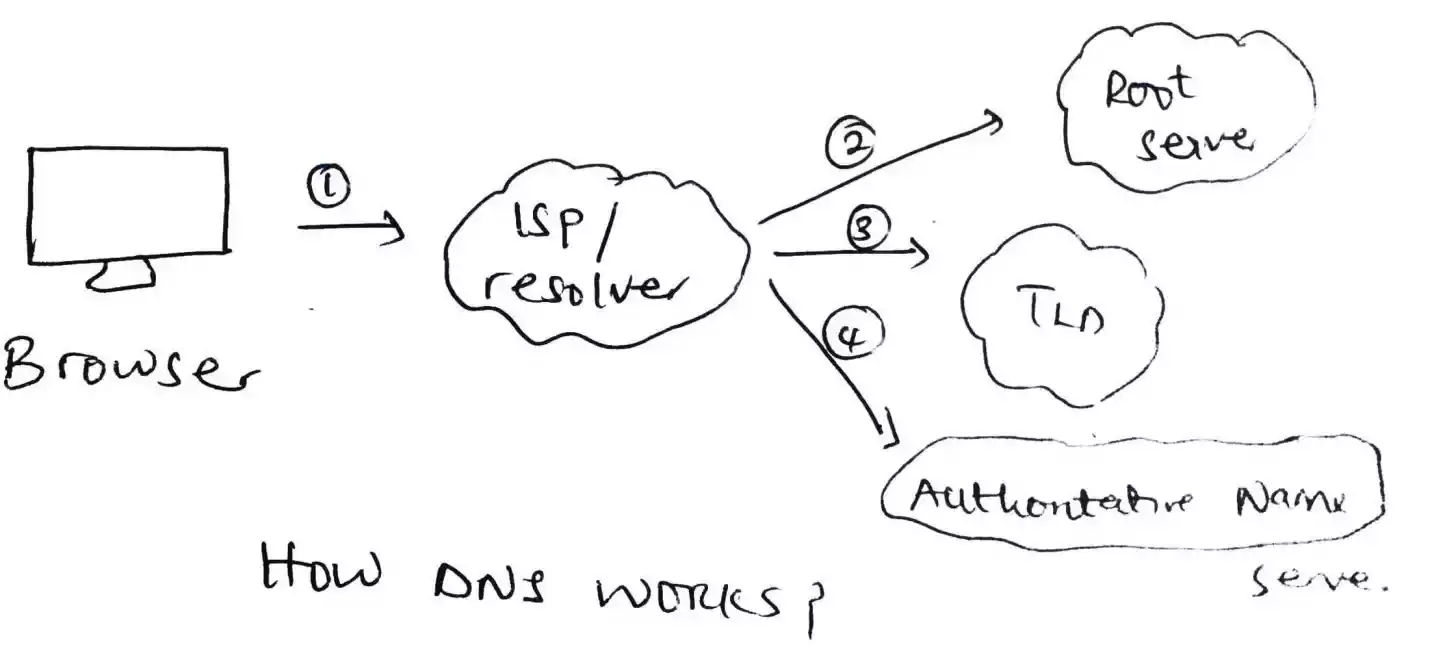
The query which is sent to the root server cannot be processed directly by the root server as it cannot understand the plain domain name so what it does is that, it directs the query sent to it to another server called TLD server (it stands for Top Level Domain server).
The resolver will then request for the IP address of the domain typed by the user from the TLD server. This TLD server is responsible for storing top level domain name with .COM, .ORG, .NET etc.
But the TLD server still cannot give a response of the IP address to the query rather, it will direct the resolver again to the last stage which is called the authoritative name server.
The authoritative name server will then give the IP address of the domain name and the resolver will store it in it cache and then tell the user’s browser “here’s the IP address and also the browser will store it in it cache and point to the intended webpage.
As you can see there are a lot of processes involved in how a DNS works.




