Multiple Access Techniques Applied by GSM
Table of Contents
What is GSM?
GSM, which stands for global system for mobile communication, is a digital cellular technology used for transmitting mobile voice and data services.
GSM uses a modulation technique called GMSK (Gaussian Minimum Shift Keying).
GMSK employs continuous-phase frequency-shift keying (CPFSK) by modulating the phase of the carrier signal with a Gaussian filter.
This method ensures smooth phase transitions, reducing spectral spreading and maintaining a constant envelope for power efficiency.
Multiple Access Techniques in GSM
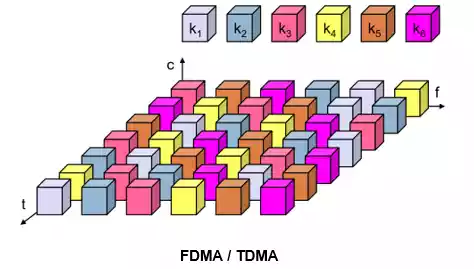
To facilitate efficient bandwidth sharing among multiple users, GSM employs or combines two major multiple access techniques:
- Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) and,
- Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA)
Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA)
The FDMA part, divides the available frequency spectrum into multiple narrower channels, assigning each user an exclusive channel for communication.
This prevents simultaneous transmission on the same frequency, minimizing interference.
Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA)
TDMA further divides each frequency channel into time slots, allowing multiple users to share the same frequency channel by occupying different time slots.
This maximizes spectrum utilization and allows more users to access the network simultaneously.
GSM Frequency Bands
GSM operates in two primary frequency bands, each with specific ranges for downlink and uplink communication:
GSM 900: This band operates in the 900 MHz range, specifically from 935 to 960 MHz for downlink (base station to mobile station) communication and from 890 to 915 MHz for uplink (mobile station to base station) communication.
GSM 1800: This band operates in the 1800 MHz range, with downlink communication allocated from 1805 to 1880 MHz and uplink communication from 1710 to 1785 MHz.
GSM Channel Allocation
Within each frequency band, GSM further divides the spectrum into smaller blocks of frequencies called carrier channels.
In GSM 900, the 25 MHz band is divided into 124 carrier channels, each with a bandwidth of 200 kHz.
The first 200 kHz channel serves as a guard band to prevent interference with adjacent services.
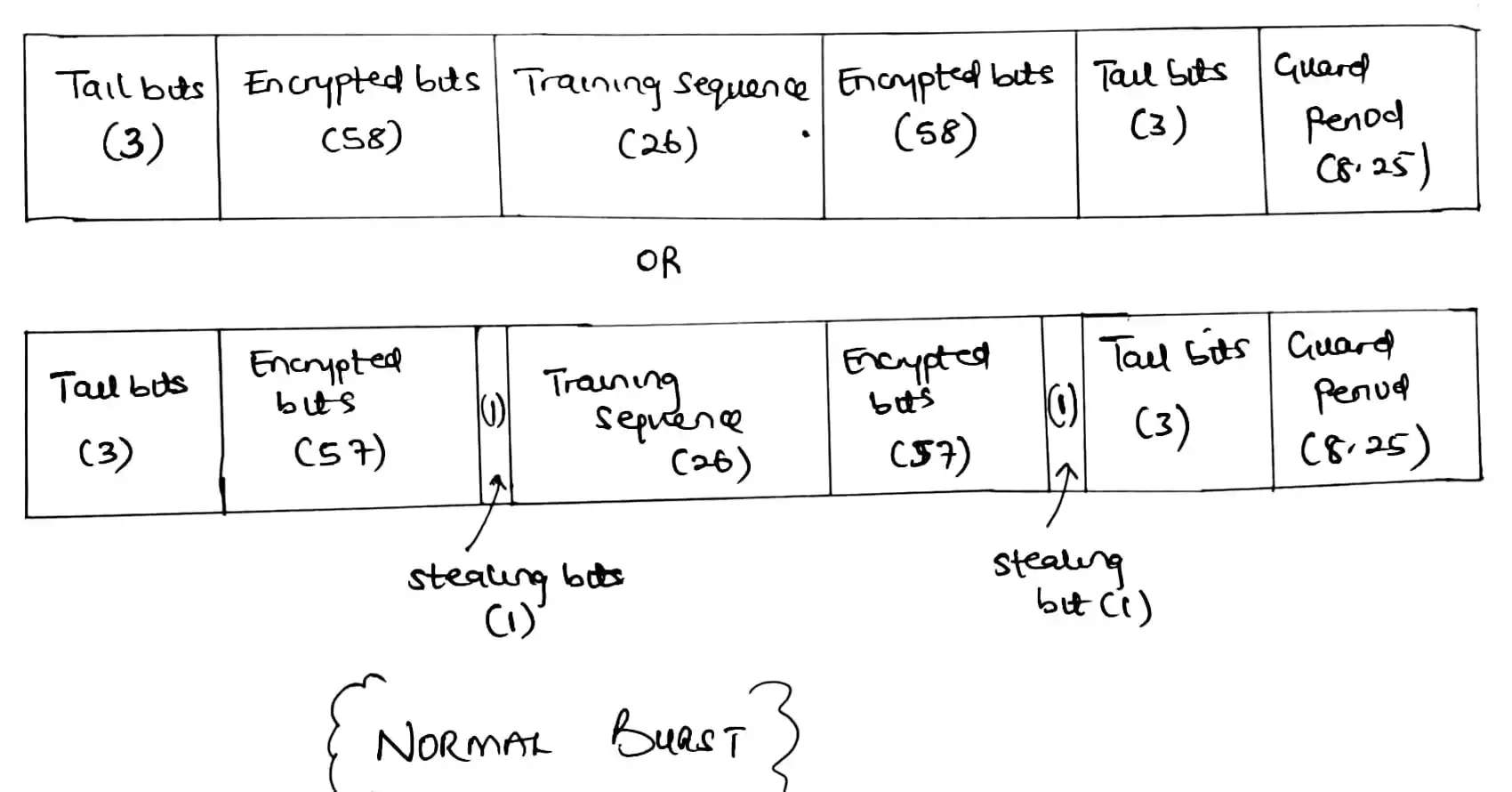
GSM Bit Rates
GSM employs various bit rates for different purposes:
Channel Bit Rate: The overall bit rate per carrier channel is 270 kbps.
Full-Rate Speech Coded Bit Rate: For voice calls, GSM utilizes a speech coding scheme that reduces the bit rate to 13 kbps.
Bit Rate per User: Each user occupies a portion of the channel bit rate, with a maximum of 22.8 kbps allocated per user.
GSM Mobile Output Power
The maximum output power for GSM mobile stations is 8 watts, with a reduced power of 2 watts for handheld devices.
In simple terms, the maximum power that GSM mobile phones can use to send signals is 8 watts.
However, for handheld devices like your typical mobile phone, this power is reduced to 2 watts.
This reduction helps conserve energy and ensures that the phone can still communicate effectively with the mobile network while using less power.
GSM Cell Radius
GSM cells, the basic coverage areas of the network, can vary in size from 350 meters for densely populated urban areas to 30 kilometers for rural regions.
This flexibility allows GSM to adapt to different deployment scenarios and coverage requirements.
FAQs
1. What is GMSK, and why is it important in GSM? GMSK, or Gaussian Minimum Shift Keying, is a modulation technique in GSM that ensures spectral efficiency by minimizing spectral spreading and maintaining power efficiency.
2. How does FDMA minimize interference in GSM? FDMA divides the frequency spectrum into channels, providing each user with an exclusive channel, thus preventing simultaneous transmissions on the same frequency and minimizing interference.
3. What are the operating ranges of GSM 900 for downlink and uplink communication? GSM 900 operates from 935 to 960 MHz for downlink and 890 to 915 MHz for uplink communication.
4. How many carrier channels does GSM 900 have, and what is the purpose of the guard band? GSM 900 has 124 carrier channels, with a guard band of 200 kHz to prevent interference with adjacent services.
5. What is the significance of TDMA in maximizing spectrum utilization in GSM? TDMA divides each frequency channel into time slots, allowing multiple users to share the same frequency channel efficiently, thereby maximizing spectrum utilization.
6. What is the maximum output power for GSM mobile stations? The maximum output power for GSM mobile stations is 8 watts, reduced to 2 watts for handheld devices.