Baseband and Broadband Transmission in Communication System Explained
Baseband and broadband transmission are ways in which digital signals can be transmitted from one point to another.
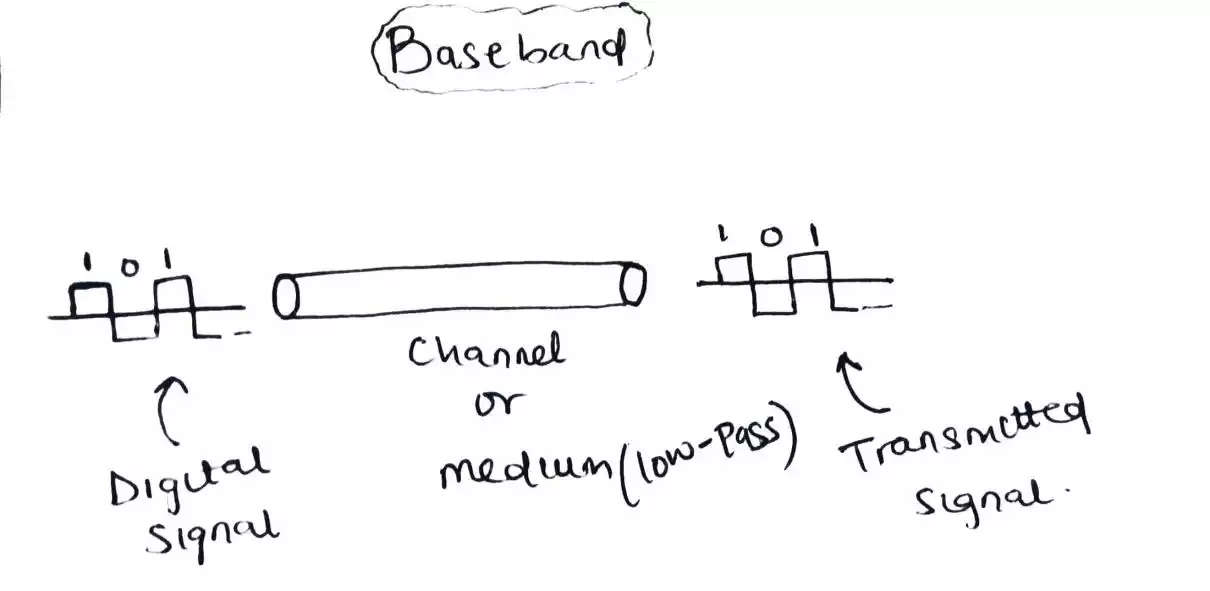
Baseband transmission
Baseband transmission refers to transmission in which a digital signal is sent over a channel without changing or converting the digital signal to an analog signal.
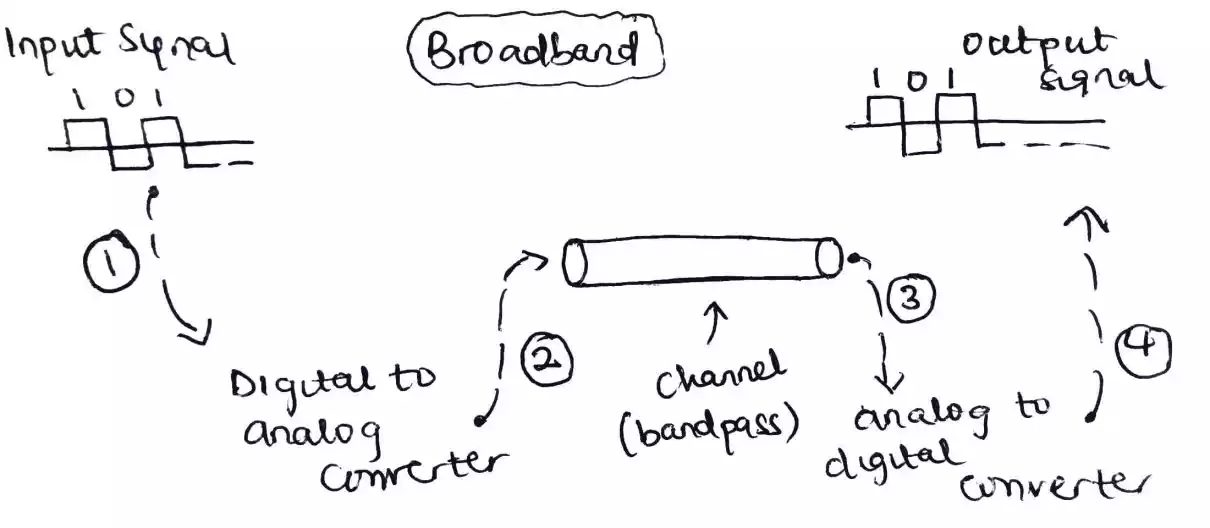
Broadband transmission
Broadband transmission sometimes referred to as modulation means changing or converting a digital signal to analog signal for transmission.
Note
The conversion from digital to analog is possible with modulation.
One factor that determines if a signal needs to be transmitted as baseband or broadband is the bandwidth.
In baseband transmission, the required bandwidth is proportional to the bit rate; if we need to send bits faster, we need more bandwidth.
Baseband transmission requires that we have a low-pass channel, a channel with a bandwidth that starts from zero while Broadband transmission requires that a bandpass channel and only an analog signal can be transmitted.
Note
A bandpass channel is a channel with a bandwidth that does not start from zero and it is limited.
In conclusion, in baseband transmission a digital signal can be directly transmitted through a channel while in broadband transmission the digital signal cannot be transmitted directly so it is first converted to an analog signal before transmission.
Reference:
📖 Data Communications
and Networking by Behrouz A. Forouzan