Types of Transmission Media in Computer Networks Explained
Computer networks, in today’s interconnected world, play a crucial role in facilitating communication and data exchange. These networks rely on transmission media to transmit data between devices.
Transmission media refer to the physical pathways or channels that enable the transfer of data signals from one point to another.
In this article, we will explore the various types of transmission media used in computer networks, their features, advantages, disadvantages, and applicable examples.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Computer Networks
Computer networks are an integral part of our interconnected world, enabling seamless communication and data sharing.
These networks consist of various devices, such as computers, servers, routers, and switches, that are interconnected to facilitate efficient data transfer and communication.
Based on their geographical scope, computer networks can be categorized into Local Area Networks (LANs), Wide Area Networks (WANs), and Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs).
Read more on: Types of Computer Networks: Their Features, Advantages, Disadvantages, and Examples
What is Transmission Media?
Transmission media in computer networks refer to the physical means through which signals are transmitted from one device to another.
It serves as a conduit for the transfer of data, allowing communication between devices within a network.
Transmission media can be categorized into two main types:
- Guided (Wired), and
- Unguided (Wireless)
Guided Media (Wired)
Guided media also known as wired media use physical cables to transmit signals. The three commonly used types of guided media in computer networks are coaxial cable, twisted-pair cable, and fiber optic cable.
1. Coaxial Cable
Coaxial cable consists of a central conductor surrounded by an insulating layer, which is further encased in a braided or foil shield.
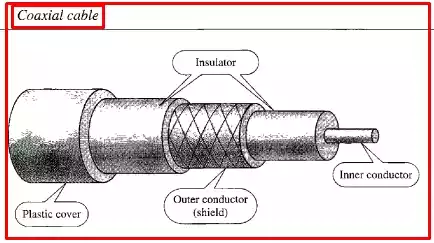
This shielding provides protection against electromagnetic interference. Coaxial cable is well-suited for long-distance transmission and offers high bandwidth capabilities.
-
Subtypes:
- Thicknet (10BASE5): It has a thick, rigid coaxial cable that supports longer transmission distances.
- Thinnet (10BASE2): It has a thinner, more flexible coaxial cable suitable for shorter transmission distances.
-
Features: Coaxial cable provides reliable transmission with high data rates. It offers excellent signal quality and supports long-distance connections.
-
Advantages: Coaxial cable is resistant to signal degradation and interference. It is suitable for applications requiring high bandwidth, such as cable television and broadband internet.
-
Disadvantages: Coaxial cable is more expensive and less flexible compared to other types of cables. It requires specialized connectors and additional grounding.
-
Applicable Example: Coaxial cable is commonly used in Ethernet networks, providing reliable and high-speed connectivity for data transmission.
2. Twisted-Pair Cable
Twisted-pair cable is made up of two insulated conductors twisted together. This design helps to reduce signal interference and crosstalk.
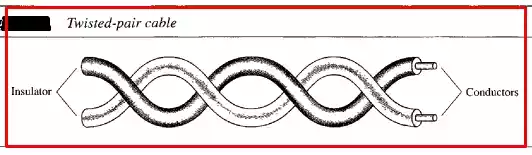
Twisted-pair cable is a cost-effective and easy-to-install medium, making it widely used in both residential and commercial settings.
-
Subtypes:
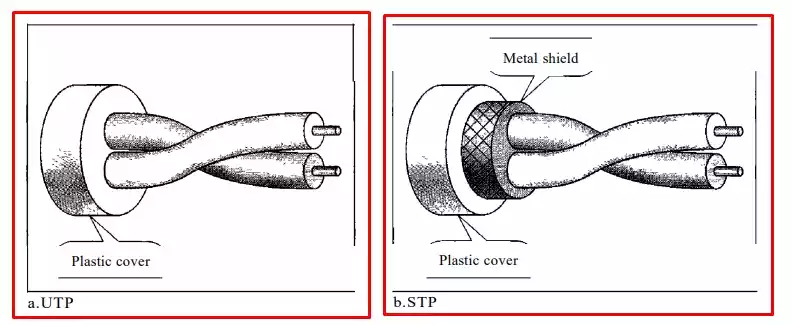
- Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP): It consists of twisted pairs of wires without additional shielding.
- Shielded Twisted Pair (STP): It incorporates additional shielding to minimize interference and crosstalk.
-
Features: Twisted-pair cable offers a balance between cost, flexibility, and performance. It supports various data rates and is suitable for short to medium-distance transmissions.
-
Advantages: Twisted-pair cable is inexpensive, readily available, and easy to work with. It provides reliable transmission in environments with low to moderate levels of electromagnetic interference.
-
Disadvantages: Twisted-pair cable is susceptible to external interference, limiting its use in environments with high levels of electromagnetic interference.
-
Applicable Example: Twisted-pair cable is commonly used in telephone networks, Ethernet networks, and home networking applications.
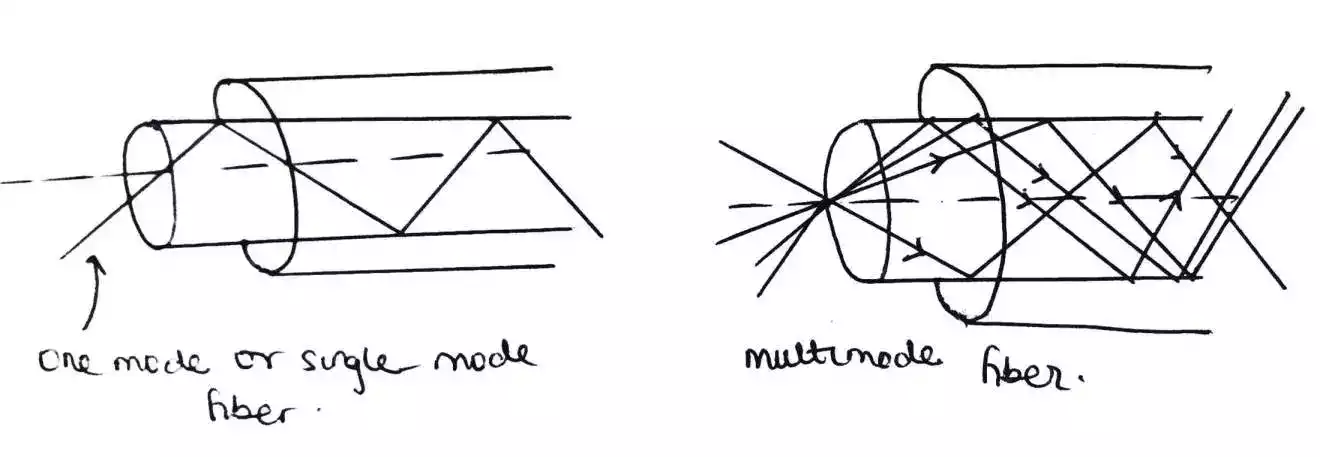
3. Fiber Optic Cable
Fiber optic cable utilizes thin strands of glass or plastic fibers to transmit signals using light pulses.
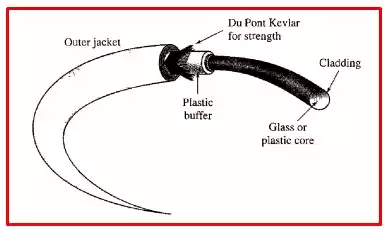
It offers high bandwidth, fast data transfer rates, and is immune to electromagnetic interference.
Fiber optic cable is known for its ability to transmit signals over long distances without signal degradation.
Read on: Why Optical Fiber Communication Is Preferred Over Other Means of Communication?
-
Subtypes:
- Single-Mode Fiber (SMF): It allows the transmission of a single light signal along a thin core, suitable for long-distance communication.
- Multi-Mode Fiber (MMF): It supports multiple light signals simultaneously, making it suitable for shorter-distance communication.
-
Features: Fiber optic cable provides the highest bandwidth and supports long-distance transmissions. It offers excellent signal quality and is immune to EMI.
-
Advantages: Fiber optic cable has a greater capacity for data transmission, provides secure communication, and is resistant to environmental factors. It is ideal for high-speed networks and long-distance connections.
-
Disadvantages: Fiber optic cable is expensive to install and requires specialized equipment for termination and splicing.
-
Applicable Example: Fiber optic cable is commonly used in high-speed networks, such as Gigabit Ethernet and Fiber Channel, where large amounts of data need to be transmitted over long distances.
Unguided Media (Wireless)
Unguided media also known as wireless media rely on radio waves, microwaves, or infrared light to transmit signals through the air without the use of physical cables. Let’s explore each subtype of unguided media.
1. Radio Waves
Radio waves are a form of electromagnetic radiation that can travel long distances. They are widely used for wireless communication, including cellular networks, Wi-Fi, and satellite communication.
- Features: Radio waves enable wireless communication over extended areas. They can penetrate obstacles and provide coverage in large geographical areas.
- Advantages: Radio waves allow for mobility and flexibility in wireless communication. They are suitable for applications requiring wide coverage, such as mobile devices and wireless networking.
- Disadvantages: Radio waves can be affected by interference, such as obstacles and other devices operating in the same frequency range. They have limitations in terms of bandwidth and data transmission rates.
- Applicable Example: Radio waves are used in cellular networks, Wi-Fi networks, and satellite communication.
2. Microwaves
Microwaves are a higher-frequency form of electromagnetic radiation that can transmit signals over shorter distances compared to radio waves.
They find applications in point-to-point communication systems and satellite communication.
- Features: Microwaves offer higher frequency ranges and shorter wavelengths compared to radio waves. They are suitable for point-to-point communication over relatively shorter distances.
- Advantages: Microwaves provide higher bandwidth and faster data transmission rates compared to lower-frequency alternatives. They are used for high-capacity communication links.
- Disadvantages: Microwaves are more susceptible to atmospheric interference, including rain fade and line-of-sight limitations. They require precise alignment and careful consideration of obstacles.
- Applicable Example: Microwaves are used in point-to-point communication links and satellite communication systems.
3. Infrared Light
Infrared light is a form of electromagnetic radiation with a shorter transmission range than radio waves or microwaves.
It is commonly used for short-range communication, such as remote controls and home automation systems.
- Features: Infrared light operates at lower frequencies and shorter wavelengths than radio waves and microwaves. It requires a direct line of sight between the sender and receiver.
- Advantages: Infrared light offers secure communication and is less prone to interference from external sources. It is suitable for short-range applications and remote control systems.
- Disadvantages: Infrared light has limited range and can be affected by obstacles or interference from other light sources. It requires a clear line of sight between devices.
- Applicable Example: Infrared light is used for remote controls, home automation, and short-range wireless communication.
Choosing the Right Transmission Media
The choice of transmission media depends on various factors, including the distance between the sender and receiver, the amount of data to be transmitted, the security requirements, and cost considerations.
It is essential to evaluate the specific needs of the network before selecting the appropriate transmission media.
Examples of Transmission Media Usage
Different types of transmission media find applications in various computer networks:
- Coaxial cable is commonly used in Ethernet networks, providing reliable and high-speed connectivity for data transmission.
- Twisted-pair cable is employed in telephone networks, as well as in certain Ethernet networks for short to medium-distance communication.
- Fiber optic cable is utilized in high-speed networks, such as Gigabit Ethernet and Fiber Channel, where large amounts of data need to be transmitted over long distances.
- Radio waves are utilized in cellular networks, Wi-Fi networks, and satellite communication to enable wireless communication over extended areas.
- Microwaves find applications in point-to-point communication links and satellite communication systems, providing high-capacity communication links.
- Infrared light is used for remote controls, home automation, and short-range wireless communication.
By understanding the characteristics and applications of different transmission media, network administrators can make informed decisions when designing and implementing computer networks.
FAQs
- What is the difference between UTP and STP cables? UTP cables are unshielded and cost-effective, while STP cables have additional shielding for enhanced protection against electromagnetic interference.
- What are the advantages of fiber optic cables? Fiber optic cables provide high bandwidth, fast data transfer rates, and immunity to electromagnetic interference. They are ideal for long-distance and high-speed networks.
- Which transmission media is best for a home network? For a home network, UTP cables (Cat5e or Cat6) are commonly used due to their affordability, ease of installation, and suitability for short to medium-distance communications.