Meaning of 1G, 2G, G, E, 3G, H, H+, 4G, 5G (Mobile Network Technology Symbols)
The symbols or letters you see near the signal bar on your smartphone indicate the type of mobile network you are connected to.
Each symbol represents a different generation of mobile technology, with each generation offering faster data speeds and more advanced features.
Meaning of 1G, 2G, G, E, 3G, H, H+, 4G, 5G
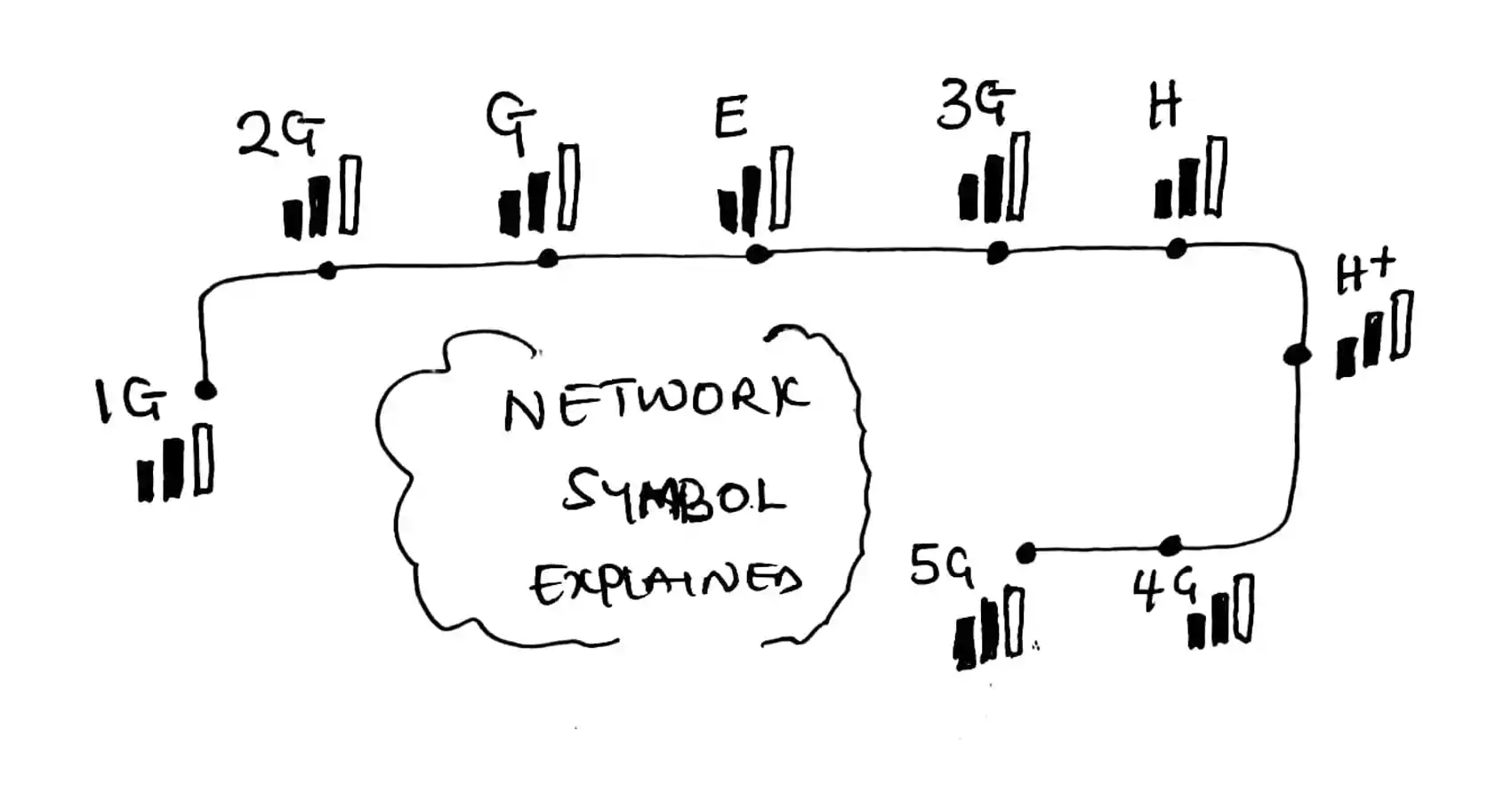
1G
First Generation mobile networks were introduced in the 1980s and were based on analog technology.
They were primarily used for voice calls and had very slow data speeds.
1G networks are not compatible with modern smartphones — so you won’t see it showing on a mobile phone.
2G
Second Generation mobile networks were introduced in 1991 and were based on digital technology.
They offered faster data speeds than 1G networks and enabled text messaging (SMS) and multimedia messaging (MMS).
The most common 2G standard was GSM, which supported speeds up to 14.4 Kbps.
G
G stands for General Packet Radio Service (GPRS), which is a 2.5G technology that was introduced around 2000.
GPRS offered faster data speeds than 2G networks and paved the way for the development of mobile internet services.
GPRS supported maximum speeds of up to 54 Kbps.
E
E stands for Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution (EDGE), which is a 2.75G technology that was introduced in 2003.
EDGE offered even faster data speeds than GPRS and was considered a transitional phase between 2G and 3G networks.
EDGE supported maximum speeds of up to 236 Kbps.
3G
Third Generation mobile networks offered significant improvements over 2G networks in terms of data speed.
3G networks supported maximum speeds of up to 384 Kbps, which enabled better browsing and multimedia streaming on mobile devices.
H
H stands for High-Speed Packet Access (HSPA), which is an evolution of 3G technology.
HSPA combined High-Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA) and High-Speed Uplink Packet Access (HSUPA) to offer substantial improvements in data speeds.
HSPA supported maximum download speeds of up to 14.4 Mbps.
H+
H+ stands for HSPA+ (Evolved High-Speed Packet Access), which is a further enhancement of HSPA. HSPA+ offered even faster data speeds than HSPA and was released in 2008.
HSPA+ supported maximum download speeds of up to 168 Mbps.
4G
Fourth Generation mobile networks were introduced in 2009 and offered significant improvements over 3G networks in terms of data speed and latency.
4G networks support maximum speeds of up to 1 Gbps, which enables seamless streaming of high-definition video and other bandwidth-intensive applications.
5G
Fifth Generation mobile networks are still under development but are expected to offer even faster speeds and lower latency than 4G networks.
5G networks are also expected to support a massive number of connected devices and enable new applications, such as the Internet of Things (IoT).