Difference Between Stranded Wire and Solid Wire
When it comes to electrical wiring, the choice of wire type can be as critical as the wiring itself.
Stranded wire and solid wire are the two primary options, each with its own set of characteristics and applications.
In this article, we will look at the difference between the two.
Table of Contents
What Is Stranded Wire?
Stranded wire, presents a more complex structure. It consists of multiple thin wires twisted together into a bundle, rendering it highly flexible and delicate.
This flexibility makes stranded wire the go-to choice for applications requiring bending and twisting, such as car doors.

Advantages of Stranded Wire:
- Stranded wires are highly flexible and can be easily bent to fit various applications.
- These wires are malleable, making them adaptable to different shapes and configurations.
- Stranded wires are known for their delicate nature, which is often beneficial in applications requiring fine or intricate wiring.
Stranded wire’s flexibility and versatility make it suitable for indoor applications, where its primary concern is flexibility.
It’s commonly found in circuit boards, computers, car wiring, electrical machinery, and more.
However, stranded wires are relatively more complex and can be affected by adverse weather conditions.
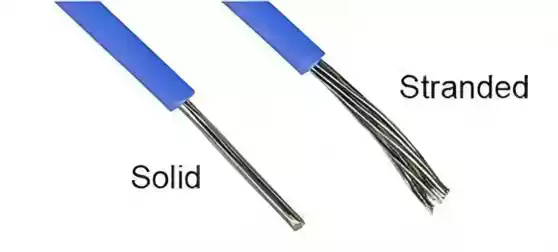
Image Credit: Univesal Network
What Is Solid Wire?
Solid wire, as its name suggests, comprises a single, unbroken conductor typically crafted from solid copper or another metal.
This wire type boasts robustness and is ideal for applications demanding high current capacity, minimal movement, and extended lifespan.
Advantages of Solid Wire:
- Solid wires are resilient in various weather conditions, making them suitable for outdoor use.
- These wires are known for their long-lasting performance and ability to withstand wear and tear.
- Solid wires have a natural resistance to corrosion, ensuring a longer lifespan.
- They are cost-effective and offer good value for various electrical applications.
Solid wires find their place in various applications, including building infrastructures, outdoor and heavy-duty settings, and vehicle controls, among others.
However, it’s worth noting that solid wires tend to be heavier due to their construction.
Key Differences Between Stranded and Solid Wires
Here is a table showing the main differences between stranded and solid wires:
| Basis of Difference | Stranded Wire | Solid Wire |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | It is composed of a bundle of twisted thin wires | It is composed of a single, solid metal conductor |
| Flexibility | It is highly flexible and can easily bend | It is stiffer and less flexible |
| Current Capacity | It has lower current capacity compared to solid wires | It can efficiently carry high current |
| Corrosion Resistance | It is prone to outdoor corrosion | It is resistant to indoors and outdoors corrosion |
| Electrical Resistance | It has higher electrical resistance | It has low electrical resistance |
| Voltage Drop | There is presence of higher voltage drop | There is low voltage drop due to low resistance |
| Termination & Connection | Termination or connection can be a bit complex | Termination and connection can be a bit easier and precise |
| Frequency Performance | Adequate performance at various frequencies | Good at high frequencies |
| Noise Generation | Generates more noise with significant attenuation | Low noise with minimal attenuation |
| Suitable For | Short-distance applications, where flexibility is crucial | Long-distance power transfer due to low voltage drop |
| Cost | Slightly higher cost | Cost-effective |
| Common Applications | Mainly used in electronics, circuit boards, and flexible applications | Used indoors and outdoors where high current capacity is required |
FAQs
- What is the primary distinction between stranded and solid wires? Solid wires consist of a single, unbroken conductor, while stranded wires comprise multiple thin wires twisted together into a bundle.
- Which wire type is more flexible, and where is it commonly used? Stranded wires are more flexible and are typically used in applications that require bending and twisting, such as in electronics devices and circuit boards.
- When should I choose solid wire over stranded wire? Solid wire is a better choice when high current capacity, durability, and resistance to corrosion are essential, making it suitable for outdoor and heavy-duty applications.
- What are the advantages of stranded wire over solid wire? Stranded wire offers exceptional flexibility, making it ideal for applications involving movement. It is also more malleable and delicate.
- Are there any disadvantages to using stranded wire? Stranded wire can be more complex and is susceptible to corrosion when used in outdoor settings.
- How does the current carrying capacity of solid wire compare to that of stranded wire? For the same wire size, solid wire can typically carry more current than stranded wire.
- Which wire type is more cost-effective? Solid wires are generally less expensive than stranded wires due to their simpler construction.





